Pathophysiology Of Cataract
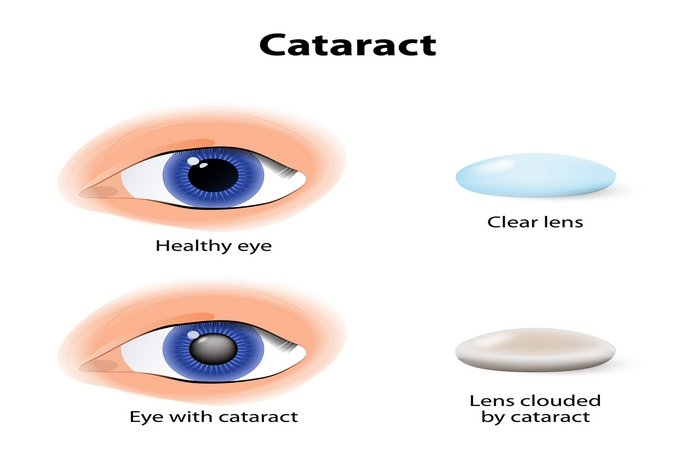
The lens is composed of a complex array of protein fibers. These proteins are known as ‘crystallins.’ These proteins are arranged in a way that gives the lens its transparency. These proteins are also protected by chemical groups that help neutralize oxidative damage caused by metabolism, UV radiation and other factors. These proteins can degenerate with age.
- The loss of transparency can be caused by either a disruption in the structure of proteins
- Or, an inability of the lens to cope effectively with oxidative stresses, leading to oxidative damage.
The proteins in the lenses clump up, and new fibers can be introduced from the peripheral edge of the lens. The lens can thicken or become pigmented.
