What You Should Know About Osteoarthritis (OA)
For research purposes, osteoarthritis is defined at multiple levels, including clinical and radiological basis. This definition serves as the premise for disease diagnosis. Clinical premise entails a collection of symptoms, such as pain, morning stiffness, warm and tender joints, etc.
On x-rays of the affected joints, a radiological set of criteria entails the presence of certain changes in the joint spaces and bones. The disease is characterized by the fact that the radiological indications of bone and joint lesions may not always correspond with the clinical symptoms.
The study of epidemiology
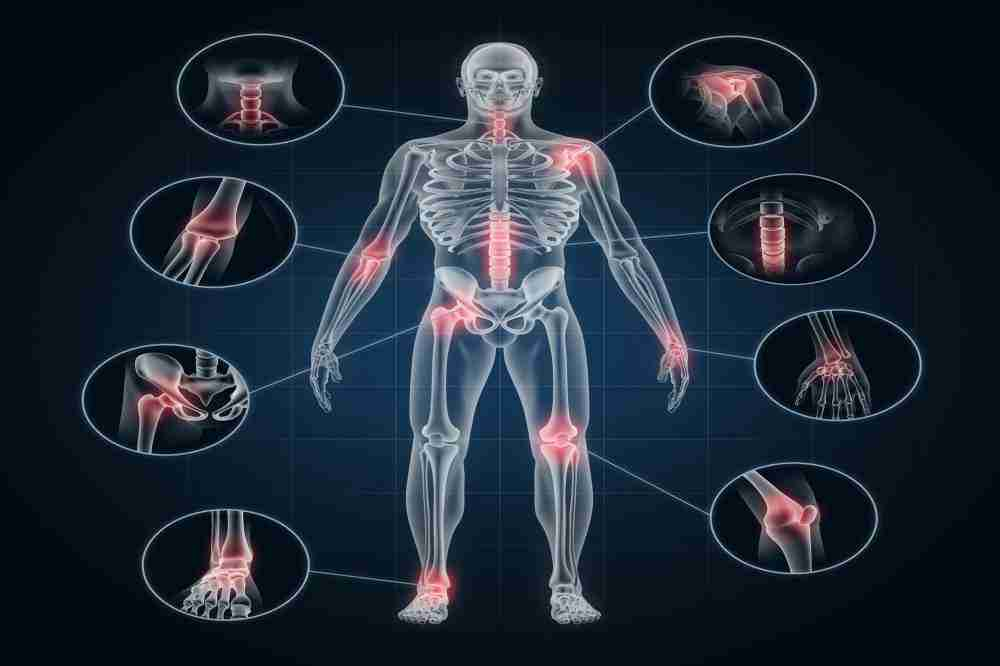
In contrast to the previously held belief that osteoarthritis was caused by trauma or aging, its origin and epidemiology are now understood to be multifactorial. The number of patients increases in the population of middle age. Given the large distribution, it is also perceived to be more strongly associated with females; males are not viewed as an exception. Osteoarthritis affects nearly 80 percent of the population older than 75. Later in the article, other factors such as trauma, sports participation, environmental factors, and the role of genetic components are discussed in greater detail.
