Do I Require Surgery To Treat Osteoarthritis?
Any competent physician will inform you that surgery is the final option when all other treatments, medications, and procedures have failed to control the disease. Surgical options are presented to symptomatic patients whose condition is deteriorating and whose damage to adjacent muscles and nerves is deemed to be progressive.
Surgical procedures can be conservative or radical. Conservative surgical procedures preserve the joint and entail minimal area reshaping. The radical approach is an aggressive one, but it is frequently required in cases of total joint involvement. It entails extracting and replacing the entire joint. Each has its own set of indications and contraindications.
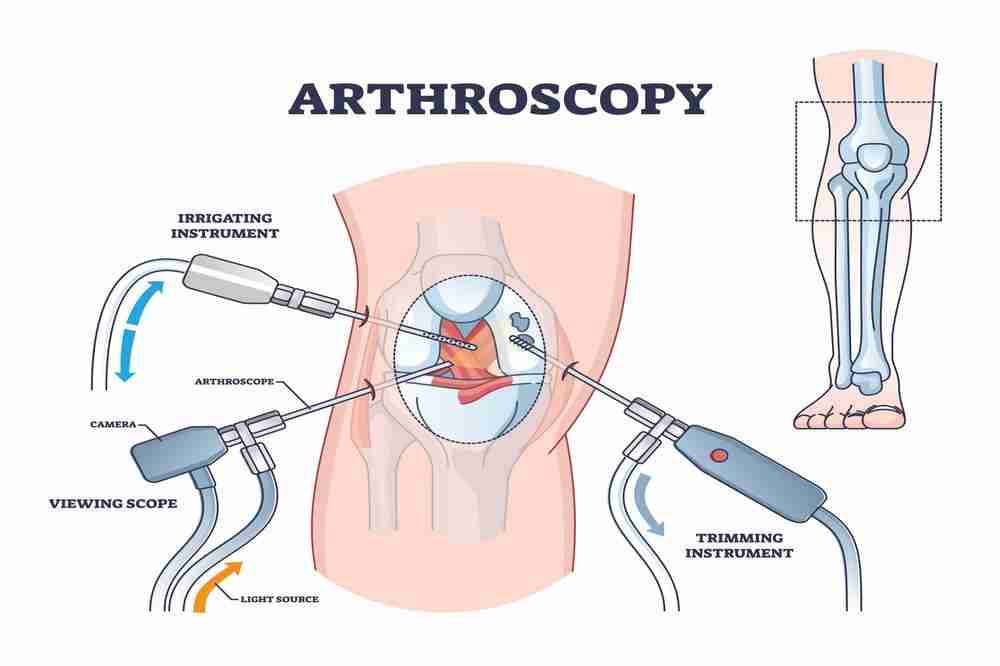
Knee arthroscopy
It is a straightforward procedure that can be performed in an OPD. A camera-guided probe is inserted through small incisions in the affected joint’s epidermis. The instruments can then be utilized to obtain a clear image of the joint’s features. The identical procedure can be utilized in the following therapeutic applications:
Debriding the bony protrusions, smoothing the bone and joint surfaces, and then cleaning the joint with an antiseptic solution.
To repair any cartilage tears.
Under the influence of inflammatory mediators, the proliferating synovium can be resected to reduce symptoms and disease progression.
To repair the meniscal tears brought on by the increased joint burden.
Take care of any bony-cartilage growths around the joint.
This surgical procedure is minimally invasive and has a very brief recovery period. However, it will not be effective in treating severe joint involvement, which requires a more radical approach.
Ostectomy procedures
This operation is somewhat more aggressive than an Arthroscopy. In the majority of patients, this procedure is recommended to purchase time for hip and knee replacements. Using a conservative surgical approach, this can offer pain relief.
This surgical procedure involves exposing the joint area and realigning the bones at the joints. In osteoarthritis, bones become deformed, which may result in aberrant deviation, as in the case of osteoarthritis of the big toe or knee. This procedure involves the use of surgical saws to remove superfluous bony outgrowths that may be causing the bone to deviate. In addition, surgical fasteners are used to secure the bone in its new position. The entire operation is performed after numbing the surgical site.
In this case, the recovery period is a bit prolonged and may be accompanied by pain. The joint also requires rest, so physical mobility may be limited until complete healing has occurred. In the post-operative period, painkillers and antibiotics must be used.
articular replacement
Joint replacement is the final treatment for painful joints caused by OA. The most prevalent indication for this procedure is osteoarthritis. This invasive procedure involves cutting, debriding, and removal of the previous joint surfaces. Metal or plastic prostheses are then inserted in place of the original. This is maintained with surgical cement.
Recuperation requires hospitalization and close monitoring. Physical rehabilitation is strongly recommended for rehabilitating the new joint.
