Diagnostic criteria for Peripheral Neuropathy
Physical exam and medical history are the most common diagnostic methods for peripheral neuropathy. Your physician will inquire about your symptoms and search for indicators that may indicate peripheral neuropathy. Additionally, he or she may prescribe tests to confirm the diagnosis. (5)
Blood exams
There is no definitive test for peripheral neuropathy diagnosis. However, blood tests may be utilised to rule out certain possible causes of the condition. Certain hormones and proteins in the blood may be associated with certain types of peripheral neuropathy, which can be measured by these assays. They can detect vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, and aberrant immune function, all of which are potential diabetes causes.
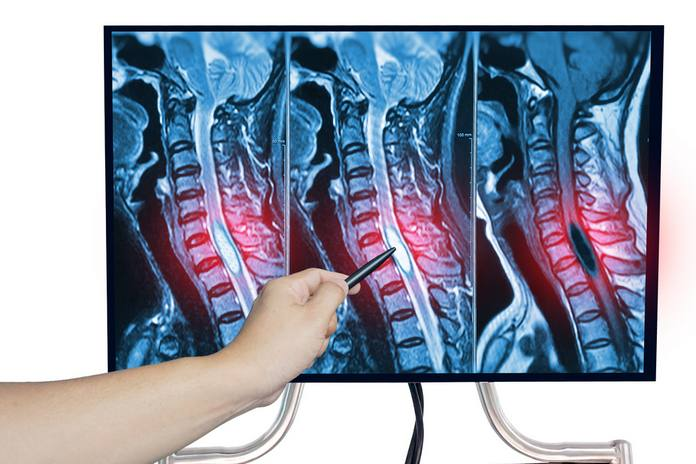
Imaging studies
Multiple imaging procedures can be used to diagnose peripheral neuropathy. Neuropathy may be caused by lesions or tumours in the brain or spinal cord, which can be detected using MRI and CT imaging.
Nervous system testing
An examination of nerve conduction measures the velocity and intensity of electrical signals as they travel along nerves. Electromyography (EMG), which analyses the electrical activity of muscles, is another common test.
Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle activity.
It is a diagnostic instrument used to evaluate the health of muscles and their controlling nerve cells. Peripheral neuropathy, a disorder of the peripheral nerves, can be diagnosed using EMG. Hands and feet may experience paralysis, numbness, and pain due to peripheral nerve damage.
Small (thin, sterile) probes are inserted into the muscle during an EMG, and the electrical activity of the muscle is then monitored. This can help determine if the nerve cells that control the muscle are damaged. EMG can also be used to evaluate a patient’s peripheral neuropathy treatment response.
Studies of nerve conduction (NCS)
Nerve conduction investigations are frequently used to diagnose peripheral neuropathy. This test assesses the velocity of nerve-conducted electrical impulses. This information can help physicians determine whether nerve injury has occurred and, if so, its location. Studies of nerve conduction can also help determine the type of peripheral neuropathy a patient has.
a nerve biopsies
It is a clinical procedure involving the removal of a small portion of nerve tissue for microscopic examination. This can be used to diagnose peripheral neuropathy and identify its underlying cause.
