Peripheral neuropathy causes
The possible causes include: (4)
Facial ptosis
Facial palsy is a condition that prevents the facial muscles from moving. This can result in difficulties with facial expressions, speech, and feeding. Facial palsy can be caused by a variety of factors, including a stroke, brain tumour, or birth injury. It can also be brought on by peripheral neuropathy, a disorder of the nerves that regulate the muscles. The treatment for facial palsy varies based on the underlying cause. Some patients with this condition may require surgery, while others may only require physical or speech therapy.
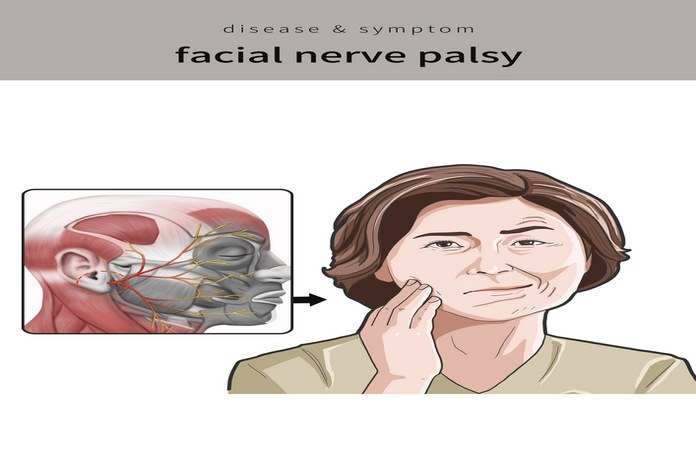
The condition of Bell’s palsy
Bell’s palsy is a form of peripheral neuropathy that effects the facial nerve or 7th cranial nerve. The condition causes facial paralysis or muscle weakness on one side of the face. It can also affect the eyes and cause problems with the production of tears and secretions. In most cases, Bell’s palsy resolves within a few weeks or months, but it can sometimes be a permanent condition. Bell’s palsy has no known cure, but there are treatments available to alleviate symptoms and promote rehabilitation.
Ulnar neuropathy
The ulnar nerve is affected by the peripheral neuropathy known as ulnar nerve palsy. This form of neuropathy can cause hand and arm weakness, numbness, and tingling. The ulnar nerve is a long nerve that runs from the shoulder to the hand via the arm and forearm. It regulates movement and sensation in the hand and fingers, as well as certain arm muscles.
Radial neuropathy
Radial nerve palsy effects one of the three major nerves in the arm, the radial nerve. The radial nerve supplies the back of the hand, wrist, and forearm with sensation and movement. Patients with nerve damage in these areas may experience numbness or weakness. Radial nerve palsy can be brought on by trauma, such as a fractured bone near the elbow, or by diseases such as diabetes or stroke. Depending on the specific underlying cause of the nerve injury, treatment may include strengthening and range of motion exercises, arm braces or splints, or surgery.
Sciatic nerve pain
Sciatica produces leg pain, numbness, and tingling. This is because the sciatic nerve, which travels down the back of each leg from the lower back, can become irritated or compressed. When this occurs, peripheral neuropathy may result.
There are numerous causes of peripheral neuropathy, such as diabetes, alcoholism, infections, autoimmune disorders, and toxic exposure. However, one of the most prevalent causes is nerve damage caused by compression or irritation. This is a possible consequence of sciatica.
Carpal tunnel disorder
CTS is a prevalent, painful, and potentially disabling condition caused by pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist. The primary symptoms are numbness and tingling in the hand and digits, particularly the thumb, index finger, and middle finger. CTS can also cause pain in the hand and wrist, hand weakness, difficulty grasping objects, and dexterity issues.
The majority of cases of CTS are caused by compression of the median nerve by the carpal ligament. This ligament connects the underside of the carpus (wrist bone) to the bones at the base of the palm. When it constricts or swells as a result of inflammation, it presses on the median nerve.
Diabetic nerve damage
Diabetic neuropathy is nerve injury that can develop in diabetic patients. This condition affects nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral neuropathy is the most prevalent form of neuropathy caused by diabetes. It can cause foot and hand pain, paralysis, tingling, and other symptoms.
The disease Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a rare, systemic autoimmune disease characterised by the formation of granulomas, which are tiny nodules. The lungs, lymph nodes, eyes, and skin are the most common locations for the formation of these granulomas. Depending on which organs are affected, sarcoidosis can produce a broad spectrum of symptoms. Fatigue, fever, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and weight loss are among the most common symptoms. In some instances, sarcoidosis can also result in peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterised by nerve injury that impairs sensation and movement. Although the cause of sarcoidosis is unknown, it is believed that an overactive immune system is to blame.
Lyme illness
Lyme disease results from an infection induced by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is transmitted to humans by infected blacklegged ticks. Multiple symptoms of Lyme disease include fever, headache, and fatigue. A characteristic skin lesion known as erythema migrans is the defining sign of this condition. Infection can spread to joints, the heart, and the nervous system if left untreated. The treatment for Lyme disease is antibiotics.
Neuropathy of the extremities is a frequent complication of Lyme disease. It can cause tingling in the hands and feet, as well as paralysis and pain in the muscles. Some individuals with peripheral neuropathy also struggle with their balance and coordination. In most cases, peripheral neuropathy is treated with antibiotics to address the underlying infection and medications to improve nerve function.
Guillain-Barré disorder
It is a rare disorder that causes peripheral nerve inflammation and injury. These nerves regulate the body’s muscles and sensory organs. Arms and legs may experience muscle weakness, tingling, or neuropathy due to GBS. In some instances, it can result in paralysis. GBS has an unknown aetiology, but it may be precipitated by a viral infection or surgery. Antibiotics, intravenous fluids, and plasma exchange therapy are administered to alleviate symptoms of the disease. The majority of patients with GBS recover completely, but some may experience permanent nerve injury.
Erythema zoster
Herpes zoster, also known as shingles, is a nerve-affecting viral infection. The same pathogen that causes chickenpox causes this condition. Herpes zoster frequently causes peripheral neuropathy, which is nerve injury in the extremities. This can result in pain, tingling, and paralysis in the affected areas. Herpes zoster can also result in additional complications, including eye problems and skin lesions. Herpes zoster is treated with antiviral medications and painkillers.
Absence of vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin found primarily in animal products like meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy products. Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation and the metabolism of protein and carbohydrates. It also promotes a healthful nervous system. Vitamin B12 deficiency may result in peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy is a nerve disorder that causes tingling, numbness, and difficulties with balance and coordination in the hands and feet.
Vegans, those who have undergone gastric bypass surgery, and those who take certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, are at risk for B12 deficiency. B12 deficiency symptoms are treatable with supplements or injections.
The disease of alcoholism
Alcoholism can result in peripheral neuropathy by causing nerve damage. Alcohol-related peripheral neuropathy is characterised by paralysis and tingling in the extremities. In these areas, you may also experience pain, searing sensations, or weakness. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is imperative that you see a doctor immediately. Alcoholism-induced peripheral neuropathy can cause permanent nerve injury if left untreated.
Intravenous neuropathy
Injection neuropathy is a form of peripheral neuropathy induced by substances injected into the body. Drugs and vaccines are the most common substances that induce injection neuropathy. Injection neuropathy can result in numerous symptoms, including pain, tingling, numbness, fatigue, and paralysis. Depending on the substance injected and the injection site, the symptoms of injection neuropathy can vary.
Certain pharmaceuticals
Certain medications, including chemotherapy drugs, some antibiotics, and medications for high blood pressure or heart problems, can induce peripheral neuropathy. If you are taking any of these medications and develop peripheral neuropathy symptoms, such as paralysis or tingling in your hands or feet, consult your doctor immediately.
Certain medications can reduce the likelihood of peripheral neuropathy. For instance, if you are taking chemotherapy drugs, consult your physician about methods to reduce your exposure.
