How is Parkinson’s disease diagnosed?
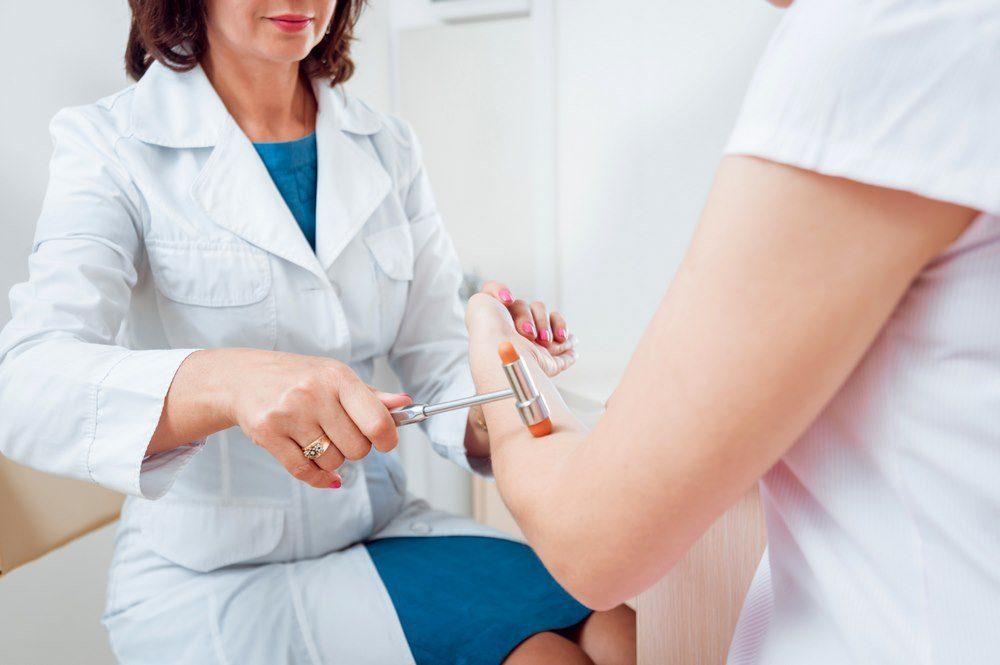
Parkinson’s is not diagnosed by a single test. Parkinson’s Disease is diagnosed based on physical examination, neurological exam, health history and review of symptoms. There is also no test that can be used to diagnose Parkinson’s. [8]
Here are some tests that can be used to diagnose Parkinson’s:
Neurological Examination
There is no one way to diagnose Parkinson’s, but there are many diagnostic tests and symptoms that can help you make a correct diagnosis. It is difficult to diagnose Parkinson’s at an early stage, but a professional can make a reasonable diagnosis by examining the motor and neurological symptoms. To diagnose Parkinson’s, two out of four symptoms must be present. Parkinson’s is diagnosed by a neurological exam if the patient has at least two symptoms.
- Bradykinesia is the slowness of movement.
- Shaking or Tremors
- Postural instability, balance issues and possible falls
- The trunk or the limbs may be rigid or stiff.
A family doctor will often diagnose Parkinson’s first. The majority of people will seek a second opinion from a neurologist who has specific training and expertise in treating or assessing Parkinson’s disease. A movement disorder specialist can help with the detailed examination of patients who have mobility symptoms associated with Parkinson’s.
