The liver
The liver is the largest organ of the body. The liver is located in the upper right quadrant of your stomach, beneath the stomach. The liver of an adult weighs approximately 3 pounds, and extends from the fifth rib on the right to the lower edge of the rib confine. The liver is divided into two projections, separated by the falciform tendons. The right flap is much larger than the correct projection. Hepatocytes are the working cells in the liver. Hepatocytes are able to regenerate themselves after liver injury. After removing a small segment of liver tissue or after causing damage to the liver, the liver can recover. The liver is a remarkable organ that can repair itself and respond to injury. However, repeated abuses and neglect can cause liver failure and death.
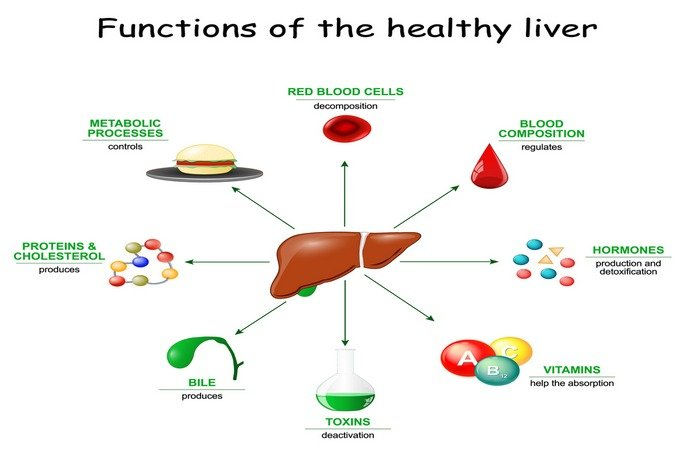
Bile is a substance that the liver excretes. It helps to divert waste products from the liver. The liver is the final stop for all blood that leaves the stomach and digestive tracts. The liver separates and balances the blood, makes supplements, and uses drugs to create structures that can be used by the rest of the body.
The liver is a vital organ with more than 500 functions. The liver is the final stop for all the blood that leaves the stomach and digestive tracts. This blood is then cycled by the liver. It balances, separates and produces supplements. It also measures different synthetic compounds and medications. The liver:
- Bile is produced to help separate fats and wastes from the small digestive tract.
- Makes certain proteins for blood plasma
- Produces cholesterol and protein to help move fats through the system
- The conversion of excess glucose to glycogen and the production of glucose varying
- The blood level of amino acids is controlled. Amino acids are the squares that make up proteins.
- Iron is stored in hemoglobin after it has been cycled.
- Converts alkali into urea which is then discharged as pee
- Removes drugs, medications and other substances from the blood
- Blood coagulation control
- Eliminating microbes and immune factors from the blood can prevent diseases.
- Removes bilirubin (bilirubin) from the blood
When the liver separates harmful substances, these wastes are discharged into bile or the blood. The waste in bile is absorbed by the digestive system and excreted from the body. The kidneys filter the blood to remove the waste.
