What is the Gonorrhea Treatment?
Following a confirmed diagnosis of gonorrhea, your healthcare provider discusses the available treatment options. Gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted disease (STD), is thankfully curable through the use of prevention and antibiotics. The most common treatment option for gonorrhea is a single injection of the antibiotic ceftriaxone and a similar dose of the oral medication azithromycin. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers well-established guidelines for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), including gonorrhea. (9)
At this time. There are no certain gonorrhea treatments that can be administered at home. Healthcare professionals and a number of epidemiology experts concur that it is essential to obtain care from a certified physician. Complications can arise if gonorrhea is left untreated, which is possible because people tend to conceal STDs out of embarrassment. These complications of untreated gonorrhea can result in negative health effects, including mortality.
Gonorrhea treatments
Cephalosporin and macrolide antibiotics are the two medication classes most commonly used to treat and cure gonorrhea patients.
Antibiotics based upon cephalosporin
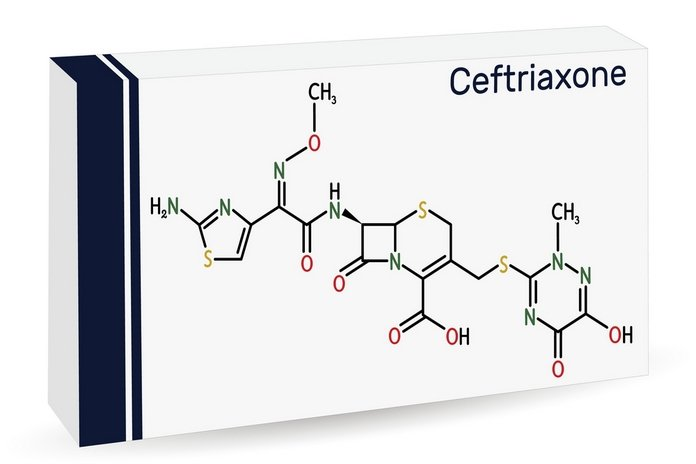
Cephalosporins belong to the class of antibiotics known as beta-lactams, which are known to kill microorganisms. Ceftriaxone, commonly known by its brand name Rocephin, is one of the most frequently used cephalosporins for the treatment of gonorrhea. Typically, a single dose of Rocephin is sufficient to treat gonorrhea. A clinician injects a single dose of Rocephin intramuscularly (IM) or intravenously (IV) into a large muscle, such as the buttocks. The injection may cause adverse effects such as shortness of breath, soreness at the injection site, rash, nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting.
Patients with gonorrhea are initially treated with cephalosporin antibiotics because the gonorrhea bacteria may develop resistance to the preponderance of other treatment options. If you are experiencing any of the potential adverse effects of the Rocephin injection or if you are not feeling well, it is imperative that you contact a doctor immediately. Prior to 2012, only gonorrhea patients received oral prescriptions of cephalosporins. However, according to the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), the CDC has updated the treatment guidelines for sexually transmitted diseases to replace oral doses with combination therapy consisting of a single dose of intramuscular ceftriaxone 250 mg and a single dose of oral azithromycin 1 g twice daily for seven days.
Macrolide antibacterial agents
In common use for the treatment of gonorrhea patients are macrolide antibiotics, particularly azithromycin, which is marketed under the brand name Zithromax. Macrolides function by inhibiting bacterial multiplication and proliferation. A single macrolide antibiotic capsule and a ceftriaxone injection are sufficient to treat gonorrhea. However, if a patient vomits within an hour of taking azithromycin, they must promptly contact their healthcare provider to determine if they require another dose of the antibiotic. As with all medications, macrolide antibiotics are associated with certain adverse effects. Headache, nausea, and diarrhea are some of the possible adverse effects of macrolide antibiotics. Some of the more serious adverse effects include edema, rash, and vomiting. However, if you experience any of these adverse effects after taking a macrolide antibiotic, you should seek immediate medical attention.
Tetracycline antibacterial agents
Similarly to macrolide antibiotics, tetracycline antibiotics in a single dose tablet in combination with another antibiotic injection of ceftriaxone may be effective in treating gonorrhea. Antibiotics containing tetracycline also inhibit the proliferation of bacteria. The antibiotic doxycycline belongs to the tetracycline class and is marketed under the brand name Vibramycin for the treatment of gonorrhea. Antibiotics containing tetracycline may cause adverse effects such as nausea, rash, and headache.
Thankfully, gonorrhea is one of the few sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that is simple to treat. After a confirmed diagnosis of gonorrhea, however, you must seek medical attention immediately. Delaying the necessary treatment for gonorrhea can result in a variety of long-term health complications for both men and women. If a person is averse to the third-generation antibiotic ceftriaxone, the combination of oral azithromycin tablets with an injection of gentamicin or oral gentamicin tablets can be beneficial. In addition, never share your prescribed medication with anyone, and if you have any drug allergies, be sure to inform your doctor. Also, discuss with your physician the potential adverse effects of the antibiotics and what to do if you experience any.
To treat infants with gonorrhea
Infants with symptoms of gonorrhea infection at birth or those at a higher risk of infection because their mother is a gonorrhea carrier are typically given antibiotics immediately after birth. In addition to preventing blindness and other severe complications of gonorrhea, gonorrhea treatment or medication does not damage the unborn child.
After remedial measures,
You and your companion must wait at least 7 days after completing your respective gonorrhea treatments before engaging in any sexual activity. The physicians also recommend that patients undergo frequent testing to ensure that the infection is eradicated completely. For gonorrhea recurrence, a second course of antibiotics is administered if:
The subsequent tests reveal gonorrhea.
There is a higher likelihood that you have gonorrhea, even if your tests indicate otherwise.
Your partner has been diagnosed with gonorrhea.
In the case of female patients, the problem of heavy bleeding or bleeding between periods must resolve prior to the next menstrual cycle. The standard recommendation of most physicians is to schedule an examination every week or two after the completion of treatment. Sexual contact is the primary cause of gonorrhea transmission, so it is crucial to refrain from engaging in intimate sexual activity with recent or current sexual partners. To prevent gonorrhea, it is also essential to request gonorrhea or other STI testing from your prospective sexual partners. (10)
