A case of blepharitis
The eyelids are folds of skin that secure the upper and lower ends of the eyes. There are also eyelashes with short, curved hair follicles on the border of your eyelids. In these follicles, oil glands can be found. Oil glands that are obstructed or irritated can lead to a variety of ocular disorders. Blepharitis, or eyelid inflammation, is one of these conditions. (1)
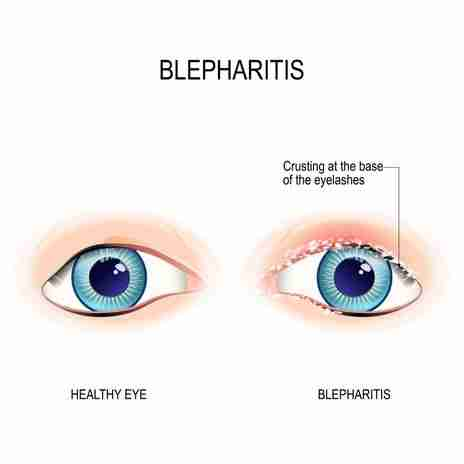
Blepharitis typically affects the margins of the eyelids of both eyes. Symptoms may include inflammation, redness, or a scorching or painful sensation. Also possible at the root of your eyelashes are flakes or oily particles (crusts). Blepharitis is more likely to affect individuals with oily skin, dermatitis, or rosacea.
Blepharitis is brought on by congested oil glands near the base of the eyelashes, which result in irritation and redness. Blepharitis can be brought on by a variety of maladies and conditions. Even though it is a chronic (ongoing) condition, you may be able to manage most cases on your own if you consult an eye care professional. Blepharitis is difficult to treat, but it is not contagious and typically does not cause permanent vision loss.
Blepharitis has two effects on the eyelids:
Anterior eyelid blepharitis – Your eyelashes are located on the exterior of your eye, where the inflammation of the anterior eye occurs. Causes of inflammation of the anterior eyelids include dandruff on the eyebrows and eye sensitivities.
Posterior eyelid blepharitis – This form of blepharitis affects the inner border of your eyelids. This form of inflammation and swelling is typically the result of a malfunctioning oil gland behind the eyelashes.
