Congenital Cataract
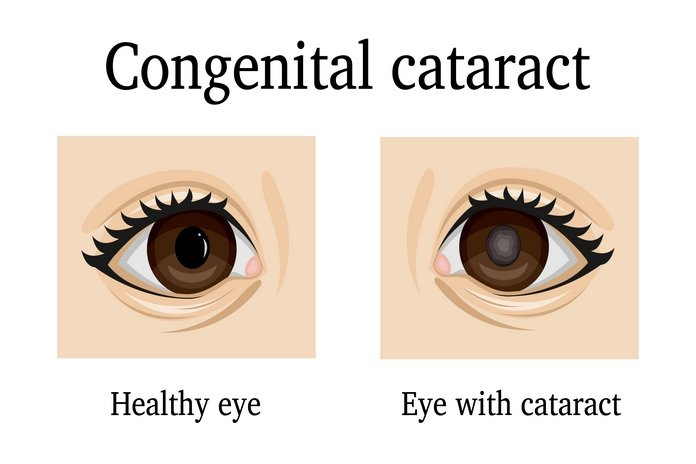
Congenital cataract is the presence of cataracts in a newborn child. Most cataract surgeries in infants are performed to prevent blindness. However, it depends a lot on the location and the opacification level of the cataract.
Classification based on causative agent of cataract.
Traumatic Cataract:
Traumatic cataract is the name given to a cataract that has been caused by a trauma. Even after many years, cataracts can form. The shape of these cataracts is either a star-shaped or rose-shaped.
Radiation cataract:
Radiation cataract is formed when the eye has been exposed to high levels of radiation, such as X rays or Gamma rays. These cataracts tend to be located at the back of the lens.
Secondary cataract:
Secondary cataract is the cloudiness of the posterior capsule. After cataract surgery, 30% of patients require treatment for secondary cataract.
Morgagnian cataract:
Hyper-mature cortical cataract is a Morgagnian cataclysm. The degeneration of proteins in the eye causes spoke-like shapes to start appearing in the eyes at the beginning of a cortical cataract.
Post-vitrectomy cataract:
During the surgery, the surgeon replaces the vitreous fluid with another liquid. After a while, the liquids begin to dissolve oxygen and break down. This leads to nuclear cataract.
