Cataract and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) treatment.
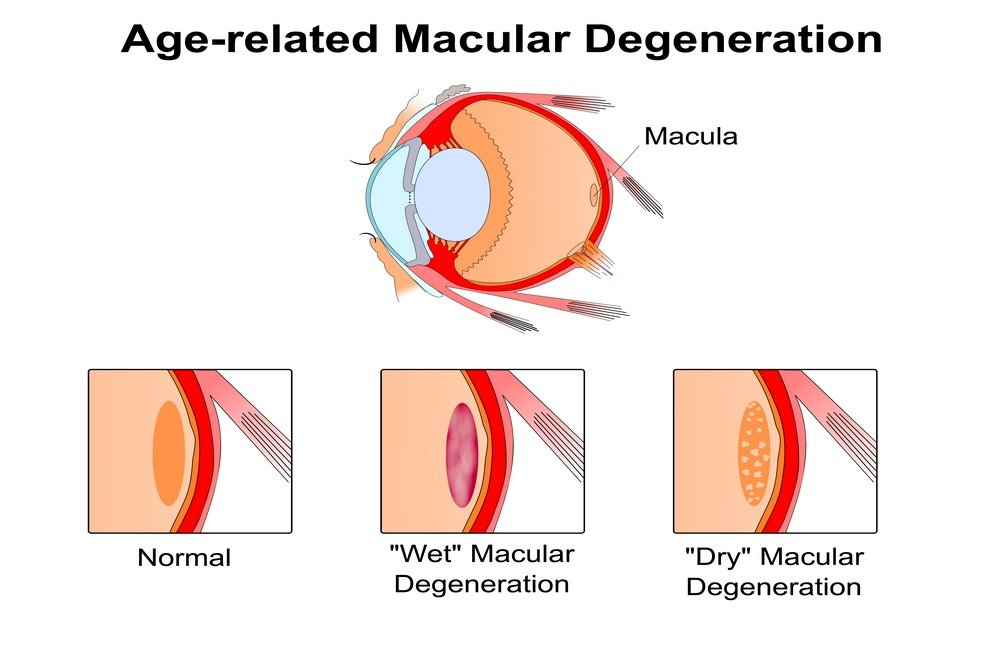
ageing is associated with vision decline. It is possible that oxidative stress contributes to the underlying causes of both diseases. Therefore, scientists are investigating the function of vitamin C and other antioxidants in the treatment of eye-health disorders. Numerous studies have investigated the function of vitamin C in cataracts and AMD. Some of these findings suggest that vitamin C intakes greater than 300 mg per day reduce the risk of developing cataracts by 75%.
All studies indicate that vitamin C may delay the progression of AMD and reduce the risk of developing the disease. Vitamin C can protect the body from the damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants such as vitamin C neutralise these free radicals by donating one of their electrons, thus terminating the electron-stealing reaction. After donating an electron, antioxidant nutrients do not convert into free radicals because they are quite stable in both forms and function as scavengers. Vitamin C prevents tissue and cell injury that could lead to cellular diseases and degeneration.
By undergoing single-electron oxidation, vitamin C reacts with free radicals to form a relatively poor reactive intermediate known as ascorbyl radical. The process of single-electron oxidation reduces free radicals to dehydroascorbate and ascorbate. Vitamin C can therefore reduce reactive and toxic oxygen species such as hydroxyl radical, superoxide anion, and nitrogen oxide radicals in the body. As the basis for the majority of vitamin C’s biological functions, the reduction of these free radicals is of critical importance.
Vitamin C also plays a crucial role in protecting other vitamins, such as vitamin E and vitamin A, from the damaging effects of oxidation. Additionally, vitamin C helps maintain healthy dentition and reverses ageing. Vitamin C also improves general physical health by removing toxic metals from the body. Vitamin C inhibits the formation of cataracts and is thus beneficial in the treatment of glaucoma.
