Folate or Folic acid, Vitamin B9
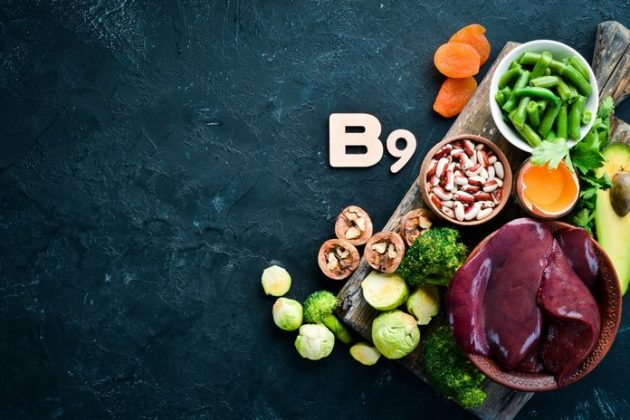
Folate or vitamin B9 is required to transport oxygen throughout the body and produce red blood cells; vitamin B9 also aids in the development of the fetal nervous system, cell proliferation, and DNA synthesis. Women of childbearing age must consume a diet rich in folate to prevent fetal growth problems.
The following foods contain folate:
Beans and lentils
Leafy green vegetables
Chicken Liver Seeds
Eggs and Cereal
Citrus produce
Folic acid poisoning
Although folic acid is generally non-toxic, excessive daily intakes of greater than 1,000 mcg can cause irritability, intestinal dysfunction, and malaise over time. The primary concern with excessive folate intake is that it can mimic a vitamin B12 deficiency; therefore, it is preferable to take these two vitamins in accordance with the RDAs.
