Toenail Fungus Indications
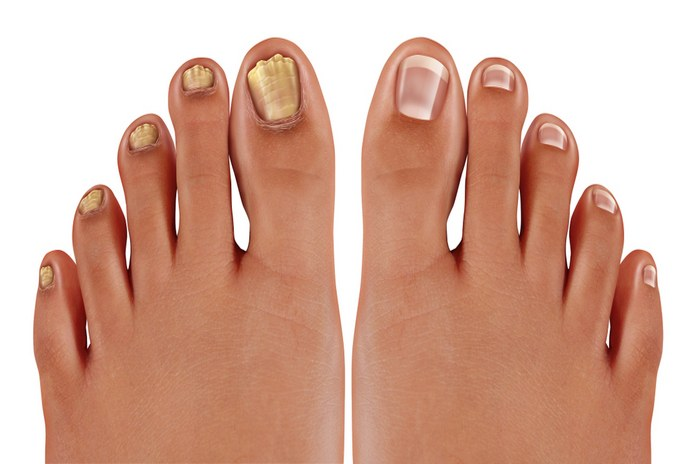
Depending on the type of fungal nail infection, the symptoms will vary. They typically begin modest and worsen.
In the outset, a yellow or white spot may be visible beneath the nail. By the time this spreads, your entire nail may become green, yellow, white, or black.
The nail may thicken and become difficult to trim.
You may also encounter a noxious odour.
Your nail may become deformed.
It may begin to spiral downwards or upwards or separate from the nail bed.
However, the nail may become crumbly and brittle upon contact.
Initially, it is simple to disregard fungal nail infections because you may not experience any pain. If left untreated, however, it may be painful to apply pressure to the portion. If an infection becomes severe enough, it may become difficult to walk. Infected fingernails are typically bulkier than normal and may have an irregular or warped shape. They may break readily. Nails affected by fungus may appear yellow. Occasionally, a white spot appears on the nail and then grows larger. When fungus forms under the nail, it may become lax and separate from the nail bed. The fungus may also extend to the surrounding skin of the nail.
The most frequent indications of toenail fungus (onychomycosis) are simple, visually and excruciatingly apparent spots. Symptoms may include thick nails, dryness, pain or a brittle texture, colour aberration or a change in the shape of the nail, a foul odour, and separation of the nail from the nail bed (onycholysis). Each nail is infected via a fissure or orifice by the fungus dermatophytes, which is the most common nail fungus. It causes the nail to become discoloured, thickened, and eventually brittle, sometimes without causing any discomfort. If the nail has been lifted from the epidermis underneath the nail bed, there may also be yellow or white spots.
The fungus could also propagate and infect additional nails. Given that many of these symptoms and indicators may also be present in other skin and nail conditions, it is recommended that the nail be examined by a medical professional. A complete diagnosis of the ailment could lead to an accurate treatment plan. A severe case of nail fungus can be excruciating and cause permanent damage to your nails. And if your immune system is compromised as a result of diabetes, medications, or other conditions, it could extend to other severe infections that affect the feet. If you have diabetes, your feet could have weak blood circulation and nerve supply. Additionally, you are at a greater risk for cellulitis (bacterial skin infection).
Therefore, any minor foot injury involving a nail fungus infection may result in a more serious complication. Consult your healthcare provider if you have diabetes and suspect you have nail fungus. Sometimes, nails with a fungal infection are:
The thickest
(Brown, yellow, or white) Discoloured
brittle or fractured
A fungal nail infection is rarely bothersome until it becomes severe. Some people with fungal toenail infections also have a fungal skin infection on the toes, particularly between the toes (commonly referred to as athlete’s foot). Multiple types of fungi (moulds or yeasts) that are naturally present in the environment can cause fungal nail infections. Small fissures in the nail or the skin surrounding the nail may allow bacteria to infiltrate and cause an infection. Anyone is susceptible to nail fungus infections. A few people, including those with the following conditions and elderly adults, may be more susceptible to developing a fungal nail infection:
Diabetes mellitus
Athlete’s foot (fungal infection of the foot)
A nail infection or nail surgery
Blood circulation difficulties
A deficient immune system
While toenail fungus is common, it is typically harmless. Symptoms primarily affect the appearance of toenails. Toenail fungus may extend to the skin between other body parts or toenails. When dressing, hosiery should be worn first to reduce the likelihood of its spread. Curing toenail fungus requires some time and is not always effective. Even after treatment, toenail fungus can recur. Discuss the benefits and drawbacks of treating toenail fungus with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action. Good foot care and hygiene reduce the likelihood that toenail fungus will return.
Regular foot examinations may help diabetics identify and treat foot problems before they become severe. You may be tempted to reshape a discoloured toenail by applying nail varnish. If you are using a conventional antifungal, you probably should not apply nail varnish. Some benefactors may advise against wearing it in any form. Polish captures moisture from the nail bed (the tissue beneath the toenail). Because fungi thrive in moist environments, nail varnish may exacerbate a fungal infection. Consequently, the nail can develop with or without polish. In uncommon instances, toenail fungus may cause an infection known as cellulitis. Without proper treatment, cellulite may pose a significant threat to your health.
If you are experiencing any of the following conditions, you must seek treatment advice from a reputable medical professional:
Discoloration near toenail
Diabetes mellitus
circulatory issues
compromised immune system
Pus or discomfort near the toenail.
If you have toenail fungus, it may be beneficial to consult your provider:
What type of infection am I suffering from?
How long will my treatment last?
Do you propose that I address it? Why or why not?
Should I be concerned about the possibility of severe complications or adverse effects?
Toenail fungus is a common infection that may be difficult to treat. The condition is typically not excruciating, but it can make you feel self-conscious about your feet’s appearance. (2)
