Toenail Fungus
The most common infection of the toenails or fingernails is a fungal infection, which can cause the nail to thicken, discolour, and become more fragile. However, infected toenails are more common than infected fingernails. The specialised term for a nail infection is onychomycosis. Under the fingernail or toenail tip, yellow or white spots are the most prevalent sign of nail fungus. Nail fungus may cause the nail to thicken, discolour, and disintegrate at the tip as the infection spreads. It may impact several digits.
If the condition is not severe or bothersome, there may be no need for treatment. Medications and self-care measures may be helpful if your nail fungus is extremely painful and causes thickened nails. Even if the treatment is successful, nail fungus can return. Another name for onychomycosis is onychomycosis. This condition is known as athlete’s foot (tinea pedis) when the fungus infects the area between the soles of the feet and the epidermis of the digits. Therefore, its alternative name is onychomycosis, and it is probably athlete’s foot.
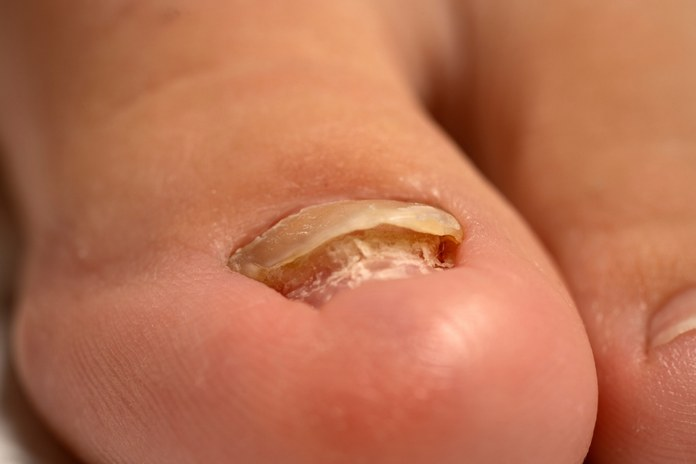
Nail infections may be caused by fungi already present on or in the body. You are susceptible to contracting a fungal infection if you come into contact with someone who has one. Your toenails are more susceptible to fungal infections than your fingernails because they are frequently enclosed in shoes and exposed to a moist, humid environment. When receiving a pedicure or manicure at a nail salon, you should consult about the cleanliness of the instruments. (1)
