Types Of Thrombocytopenia
The development of thrombocytopenia is associated with many genetic and environment factors. It has been classified into a few different categories based on the causes. Some specific types of thrombocytopenia are:
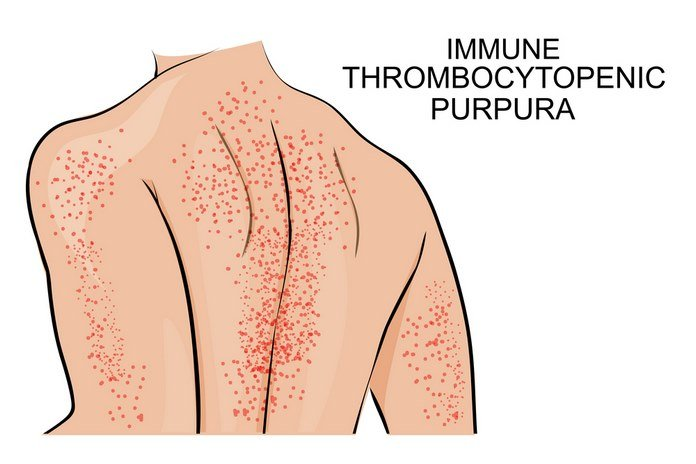
Immune-thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP).
This is a form of thrombocytopenia that occurs when the production or destruction of platelets in the bone marrow decreases. ITP is the medical term for low blood counts. ITP, or immune thrombocytopenicpurpura, can cause bruising and bleeding as well as immune reactions. ITP can be caused by antibodies. These antibodies are produced by the body in order to protect itself against bacteria and viruses. These antibodies are usually produced to prevent infection. However, they can act abnormally or affect healthy tissue. This condition is caused when immune cells, which produce antibodies, receive mixed signals. They mistakenly perceive a normal tissue to be foreign tissue and begin to reject it. In ITP the immune system recognizes the platelets as foreigners or invaders and creates antibodies against them. The antibodies destroy the platelet, and prevent its production.
Children and adults can be affected by ITP. It is more common among women in their younger years, but it’s also common in men as adults.
Chronic ITP is also possible. Chronic ITP can last for weeks or months. Common symptoms of ITP include bleeding in the nose, urine, and cuts. ITP can cause heavy menstruation in women, as well as bruises on their body.
Alcohol consumption is restricted in ITP as it can reduce the number of blood platelets and have a negative effect on their effectiveness in blood clotting. Aspirin, ibuprofen and other drugs can also affect platelet function.
