Thrombocytopenia, Overview, Types, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, Complications, Prevention, and Management
Kidney Failure
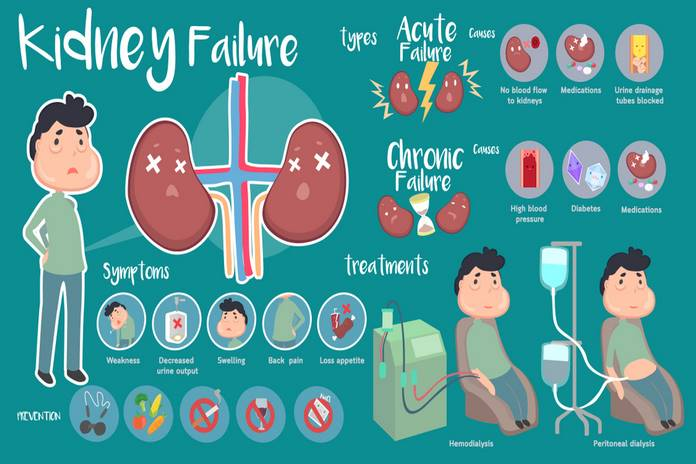
Renal failure has a strong association with thrombocytopenia. Both acute and chronic kidney failure have been shown to be associated with anemia and/or thrombocytopenia in many studies. Acute renal dysfunction causes a rise in serum creatinine. The kidneys are not working properly and waste cannot be eliminated from the body. Patients who have renal failure will need hemodialysis.
This can lead to a variety of abnormalities including bleeding and thrombotic reactions. A significant number of patients on hemodialysis have thrombocytopenia. The platelet count will decrease in patients with chronic renal disease, increasing the chances of developing thrombocytopenia. Platelet dysfunction can occur, and the patient may bleed. The study was conducted to better understand the relationship between thrombocytopenia, renal failure and thrombocytopenia. The study showed that renal failure is associated with anemia, thrombocytopenia, and other complications.
