The spread of the herpes simplex virus
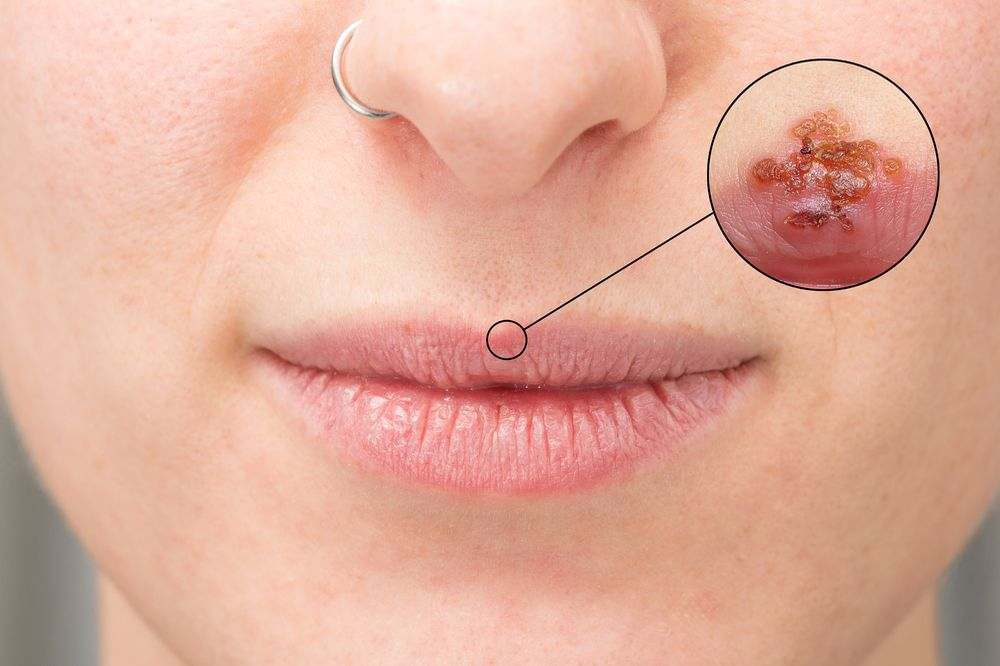
Herpes simplex viruses may propagate when they come into contact with areas of broken skin, such as the vagina, genitalia, mouth, and anus. As the herpes simplex virus is most contagious when sores are open and oozing, it can also spread when there are no sores present and the skin is entirely intact. Asymptomatic shedding refers to the transmission of the herpes virus through entirely healthy skin. Unfortunately, there is no way to rule out asymptomatic discharge, so you must always take herpes contagious. Even if no symptoms are present, herpes infection is contagious. The transmission of herpes simplex virus is usually attributable to common daily activities.
Re-infection occurs when a person touches or scratches a wound and then rubs their hand on another area of their body; this is known as re-infection. Women with vaginal HSV-2 infections can also transmit the virus to their infants via vaginal delivery during childbirth. The transmission of HSV-2 infection through vaginal delivery is more prevalent when the mother-to-be has a recent infection rather than a previous infection.
