Spinal Stenosis Diagnosis
Your doctor can diagnose spinal stenosis by examining you and looking at your symptoms. Your doctor may order other tests to determine the cause of symptoms, such as an MRI or CT scan, as well. (5)
Physical Examination
A physical exam is usually used to diagnose spinal stenosis. This includes reviewing the medical history of the patient and performing a physical evaluation of the spine. The neurophysician tests reflexes, muscle strength and any signs of spinal narrowing. The doctor may also order additional tests such as an MRI or X-ray if spinal stenosis has been suspected.
Image tests
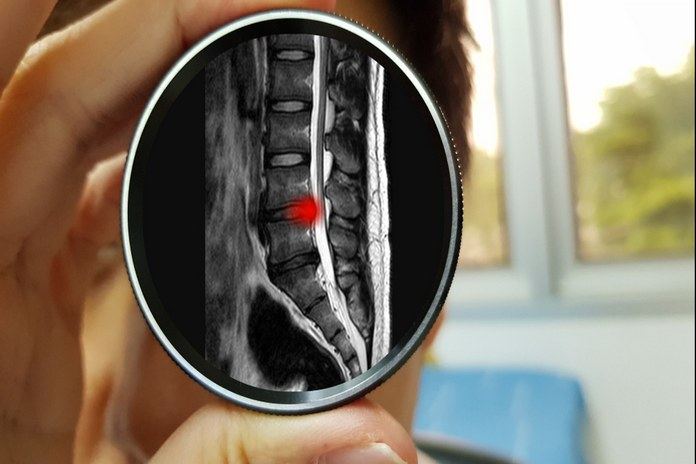
Spinal stenosis is diagnosed using imaging tests such as x rays, CT scans and MRIs.
X rays –X rays are used to diagnose spinal degeneration. Images produced by x rays allow doctors to see the size and the shape of the spine. This information will help determine if any narrowing is present. The X-ray can help identify other conditions which may be causing symptoms of spinal stenosis. They may be able see, for example, if a herniated disc or tumor is putting pressure onto the spine.
CT scan Spinal Stenosis is diagnosed by a CT scan. A CT scan creates images of the human body using X-rays. By examining the tissues and bones around the spine, it can be used to diagnose spinal stenosis. Your neurophysician can use it to see if the tissues or bones around the spinal cord have been damaged.
MRI – Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), also known as a MRI scan, is a diagnostic tool that can be used to diagnose spinal stenosis. MRI creates detailed images by using a magnetic field and radiowaves. The doctors can then see if the spinal cord is damaged or if it has been narrowed. An MRI is recommended if spinal stenosis has been suspected. This will allow doctors to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Neuronal Studies
Neuronal studies can be performed to diagnose spinal stenosis.
MyelogramA common test called a “myelogram” is a very useful tool. The test involves injecting dye in the spinal fluid, and then taking pictures of the spine. This test can identify areas of compression to the spinal cord and nerves. This test will also determine whether surgery is required to treat spinal stenosis.
Needle electromyography – A needle electromyography (EMG) test can help diagnose spinal stenosis. A thin, sterile needle will be inserted into muscles to measure electrical activity. This procedure can be used to determine the severity of nerve damage and whether it has occurred.
Nerve Conduction Study – This is a diagnostic tool that measures the speed of electrical signals along nerves. This test can be used to detect nerve damage that may be caused, for example, by spinal stenosis. The nerve conduction study, which is usually performed on the arms and legs, involves stimulating the nerve with electrodes and measuring the response. This test can be used to determine whether there is a compression of the nervous system due to a narrowing of spinal canal. This can lead to pain, numbness and weakness.
Somatosensory evoked Potentials – Spinal stenosis can be difficult to detect with standard imaging tests like an MRI or CT. A physician can order a somatosensory evoked potentia (SSEP test) to diagnose this condition. SSEP is a test that measures electrical activity of the nerves traveling from the brain to spinal cord. This test can determine if these nerves are damaged or compressed.
