Sinus Infection
A sinus infection is an inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining. The sinuses are empty spaces in the bone between your eye, cheekbones and forehead. The mucus they produce keeps the inside of your nose moist. This mucus is a reserve that protects against allergens and pollutants. Air is being pumped into healthy sinuses. Fluids can grow when the sinuses are blocked by germs. (1)
The following conditions can lead to sinus obstruction:
- Allergic rhinitis is swelling of the nasal lining caused by allergens
- Common cold
- The nasal cavity is affected by a deviated septum.
- Nasal polyps are small growths on the nasal lining.
A sinusitis is an inflammation or swelling of the tissues that line the sinuses. The four cavities (cavities), which are arranged in pairs, are called the sinuses. The small channels that connect them. The sinuses produce thin mucus which drains out of the nasal channels. This drainage helps to keep your nose clean and free of bacteria. Normaly, it is filled with air. The sinuses become blocked and are filled with fluid. It can lead to an infection. The condition is also called rhinosinusitis, where rhino means nose. If sinus tissue is inflamed, the nasal tissue will be swollen.
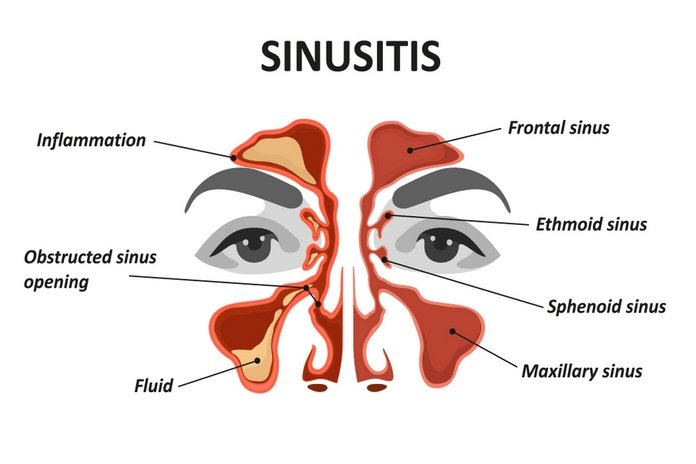
They are located in the head, near your eyes and nose. The bones that make up their structure are the reason they have this name.
- Above your eyes, you can see the frontal sinuses
- The ethmoidal synostem is located between the eyes
- The sphenoidal sinuses can be found at the back of the eye
- The maxillary sinuses are located below the eyes
It is also known as the maximumillary cavity. Anyone can get sinusitis. Individuals with nasal polyps or abnormal nose structure, as well as those who suffer from nasal allergies, asthma and nasal allergies, are more susceptible to sinusitis. You may also get sinus infections if you smoke. Around 31 million Americans are estimated to suffer from sinusitis.
There are many types of sinusitis.
- Chronic Sinusitis: The term describes a condition that includes nasal congestion, facial pain/pressure, and a decreased sense of smell lasting for about 12 weeks.
- Acute Bacterial Sinusitis:This term is used to describe symptoms such as a stuffy nose or runny nasal, facial pain, that do not disappear after 10 days. Or, the symptoms may not seem to worsen, but return to make the initial symptoms worse (also known as “double sickness”). It is effective as a decongestant and antibiotic.
- Recurrent acute Sinusitis: This term is used when symptoms occur four times or more in a year, and last less than two weeks each time.
- Subacute Sinusitis: The term is used to describe symptoms that last between four and twelve weeks.
