Complications of Pulmonary Embolization
Regular medication, including anticoagulants, can help maintain the symptoms of pulmonary embolism. However, some patients do not respond to the medication and may develop complications. Scientists are unsure of the mechanism behind pulmonary embolism. According to a study, more than 22% of people who quit taking anticoagulants after pulmonary embolism will experience recurrence. Some patients experience complications due to anticoagulants’ side effects, as they increase internal bleeding risk. Here are some of the possible complications that can arise from pulmonary embolism.
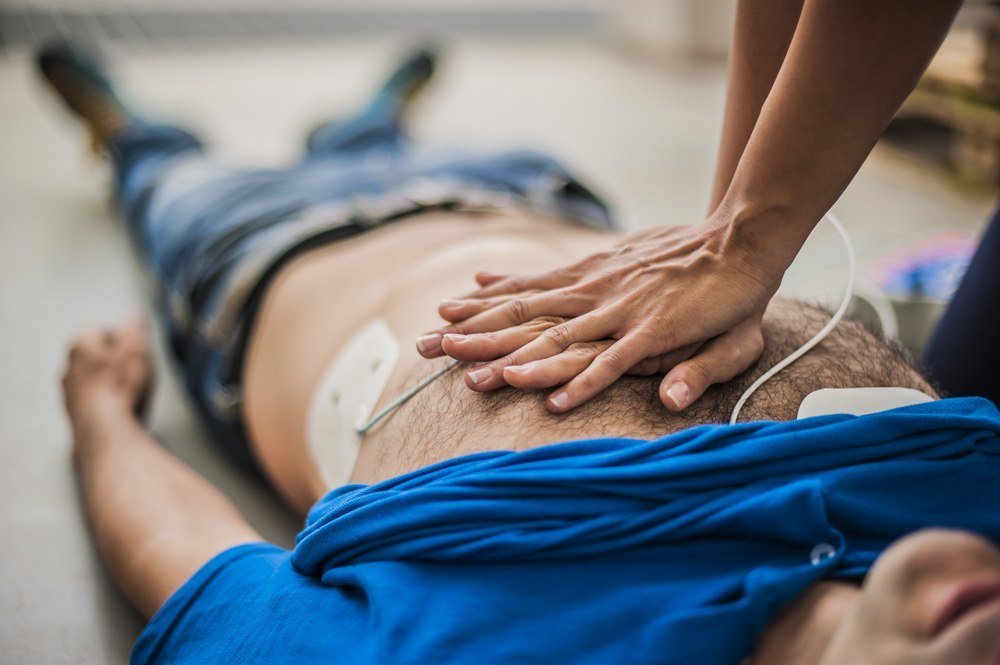
Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest occurs when your electrical system malfunctions and your heart stops beating. The electrical signals that tell your heart to stop beating are disrupted. A pulmonary embolism may cause a cardiac arrhythmia and increase the risk of death. The medical emergency of cardiac arrest must be treated immediately because it could lead to death. In emergency situations like cardiac arrest, doctors administer tissue plasminogen activater (tPA), which can be a life-saving medication. Using tPA to restore the normal heartbeat and dissolve the clot that is blocking the lungs can be life-saving.
