Complications Of Mesothelioma
As tumor cells proliferate on the membrane of the lungs and negatively impact lung function, mesothelioma symptoms worsen. The pleural effusion and shortness of breath worsen and transform into respiratory complications. The patient’s respiratory complications indicate the extent of the tumor’s growth and dissemination. As pleural mesothelioma advances to the later phases of cancer, respiratory complications become extremely prevalent among patients. Patients with mesothelioma may experience complications with respiration as a consequence of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
However, there are no specific measures that patients with mesothelioma can take to reduce or even avoid the risk of complications. Nonetheless, they can adhere to an appropriate treatment plan to reduce the likelihood of complications. There are approaches and measures that help prevent or limit mesothelioma complications, such as oxygen supplementation, respiratory exercises, and surgical palliative procedures. Utilizing appropriate surgical procedures in the later phases of mesothelioma can help alleviate symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
To detect respiratory complications in a timely manner, the patient must also disclose any changes in the functionality of the lungs, the severity of chest pain, and any other symptoms to their doctor. Among the most frequent complications of mesothelioma are the following:
Pneumopleural exudate
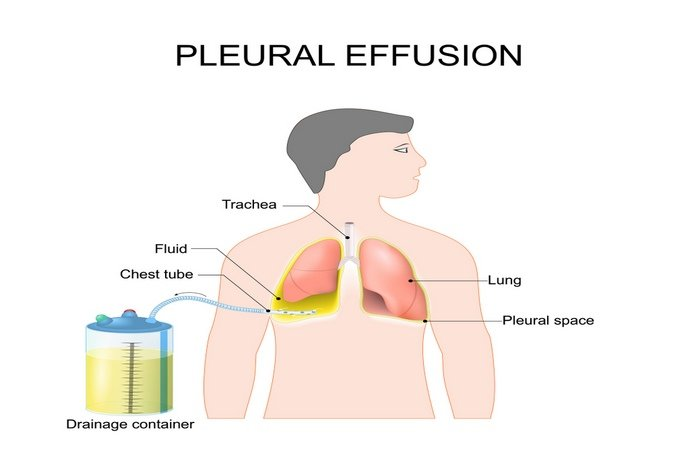
The accumulation of fluid between the layers of the pleural lining is known as pleural effusion. This fluid accumulation exerts pressure on the airways and ultimately causes breathing difficulties. In the advanced stages of their disease, nearly 90 percent of patients with pleural mesothelioma experience pleural effusions. To prevent further damage, it is essential to receive appropriate treatment for pleural effusion by draining the fluid from the pleural spaces to improve breathing and reduce lung pressure.
