Medication and Treatment (Drug list)
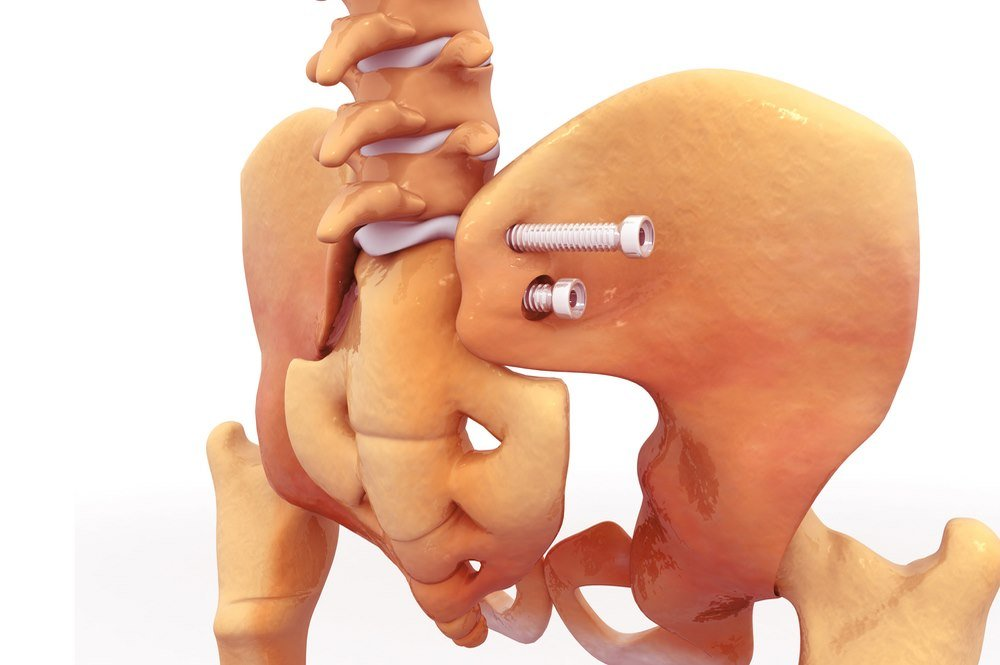
Osteoporosis progresses silently until a non-traumatic wrist, pelvic, or spinal vertebral fracture occurs. In the event that osteoporosis is discovered due to such a fracture, the immediate treatment would consist of addressing the fracture.
In treating the fracture:
The fracture is reduced by holding the broken bone in position and allowing it to regrow. This can be an arduous procedure.
Casting immobilizes the afflicted limb in order to maintain proper alignment.
Analgesics can be administered to alleviate the agony of a fractured bone.
Rehabilitation exercises mobilize muscles in order to restore functional ability. Exercises that are light and well-planned restore the bone’s weight-bearing capacity.
It can take anywhere from 6 to 12 weeks for a fracture to recover, depending on the patient’s age, gender, general physical health, and bone health.
comorbid conditions
Once the fracture has recovered, preventative medication is administered. None of the medicines listed below are curative and may cause adverse effects.
The use of bisphosphonates

In the treatment of osteoporosis, bisphosphonates are the first-line medication. They prevent bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclastic activity. This treatment method is equally effective for men and women. It can be administered orally and also as an injection. It must be consumed on an empty stomach, and food and beverages should be avoided for 30 minutes to one hour after administration.
Among the available drugs in this class are:
Risedronate Alendronate
This course of treatment takes six to twelve months, and in some cases, years, to produce the desired results.
As a rare side effect, bisphosphonates can induce osteonecrosis of the jaw bone. Before beginning bisphosphonate therapy, a comprehensive dental examination is advised.
The SERMs
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators are pharmaceuticals that help prevent bone loss by having a beneficial effect on the bone similar to that of estrogen. They contribute to bone density. Raloxifene is the only drug in this class with clinical evidence. SERMs can also cause side effects owing to the activation of estrogen receptors in various organs:
Warm flashes
Blood coagulation
Leg spasms
Hormone produced by the thyroid gland
In general, parathyroid hormones promote bone resorption, but when administered intermittently in small dosages, they can increase the osteoblasts’ activity by causing their proliferation and reducing their apoptotic death. This effect on bone density and mass is utilized in osteoporosis-treating drugs related to parathyroid hormone. Other parathyroid hormone-related or bone-building medications include:
Teriparatide is administered subcutaneously once daily for two years. It stimulates the production of new bone matrix.
Romosozumab is a relatively novel medication that is administered monthly.
All of these medications must be administered in conjunction with other anti-osteoporosis medications in order to preserve bone health. PTH therapy is not a first-line treatment and is reserved for patients who are resistant to other treatments. Nausea is a frequent adverse effect.
