Pathology Underlying Osteoporosis
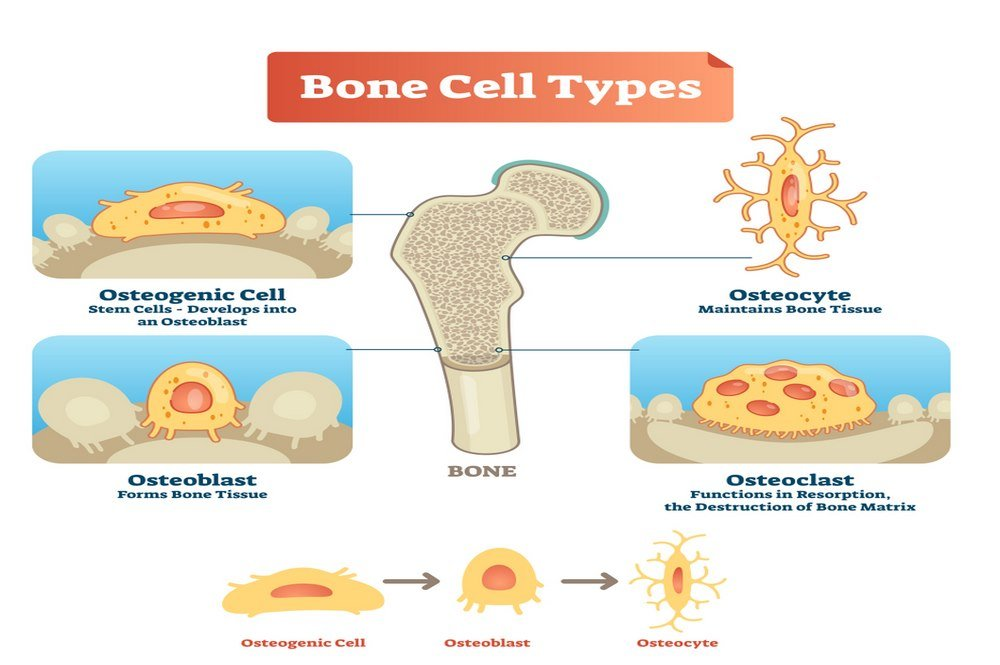
Active bone cells, osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and relatively quiescent mature cells, osteocytes, maintain the structural equilibrium of the bone. The function of osteoblasts is to deposit new bone cells into the bone matrix. In doing so, they advance through stages toward becoming completely mature osteocytes. In contrast, osteoclasts induce bone resorption. They dissolve the bone matrix in order to continue the regeneration cycle. Increased osteoclastic activity leads to bone degeneration. When this loss is not accompanied by bone formation by osteoblastic activity, an overall decrease in bone density and osteoporosis result.
Osteoporosis as opposed to Paget’s disease?

Due to their similarity in causing skeletal deformity, these two skeletal system diseases are frequently confounded. In Paget’s disease, aberrant bone architecture results from an imbalance in the activity of bone cells. It targets a limited number of bones, including the cranium, leg, forearm, and pelvic bones. In Paget’s disease, the bones become fragile and susceptible to deformities, such as the bending of long bones and the enlargement of the cranium.
