Hormone Substitution Therapy

Women going through the menopause may experience heat flashes and osteoporosis. To avoid these adverse effects of menopausal estrogen decline, some women may choose hormone replacement therapy. This procedure substitutes exogenous hormones for the diminished endogenous estrogen. This estrogen can positively influence bone homeostasis.
As a result of the increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, it is not a preferred treatment for osteoporosis. Increased blood density is another complication, which can precipitate thrombus formation and heart problems.
Calcium Medications

Calcium, the most important mineral in bones, must be maintained in order to prevent osteoporotic fractures. Maintaining a healthy level of calcium in children reduces the risk of osteoporosis by facilitating the achievement of optimal bone mass in later stages of development. Several food items are calcium-rich, but osteoporotic patients may be advised to take calcium supplements in order to satisfy the recommended daily intake of approximately 700 mg. These supplements are available as instant-use effervescent tablets. Calcium supplements pose a slight danger to the kidneys and heart.
Vitamin D Medications
Particularly in cases of senile osteoporosis or limited exposure to sunlight, vitamin D supplementation becomes essential. Additionally, pregnant and lactation women have a greater need for vitamin D. The daily requirement for vitamin D is 10 micrograms, which can be obtained through oral supplements. There are also monthly injections available.
Testosterone Treatment
Testosterone is responsible for bone growth during childhood and puberty. If testosterone levels decline with age or in obese individuals, this may negatively impact bone mineralization. In this regard, testosterone replacement therapy is one of the available treatment options. To restore testosterone levels, exogenous supplies are used. According to reports [9], the bone health indices have significantly improved after a 6-month treatment program. The findings demonstrate the importance of androgens in the formation and maintenance of bone structure.
The hormone calcitonin
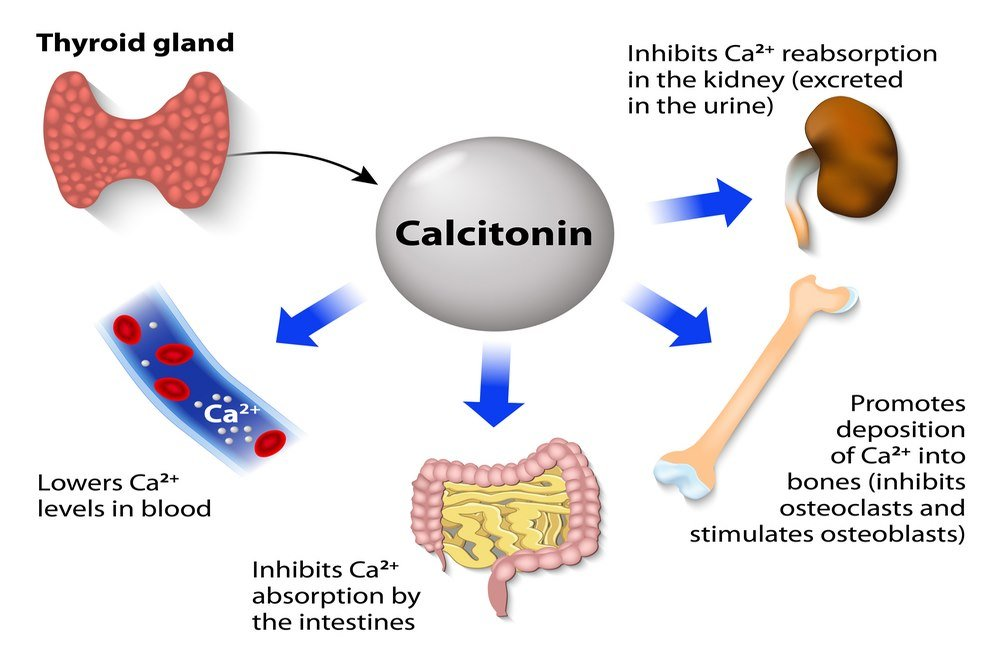
By administering exogenous calcitonin, bone mineralization can be enhanced and bone resorption by osteoclasts can be decreased. Despite not being the first line of treatment, it has proven to be effective. Salmon-derived calcitonin is commonly used because it is better tolerated by humans and more effective. Primarily, long-term treatment regimens have reduced the risk of vertebral fractures [10]. Other fracture risk is affected minimally. Calcitonin bonds to its receptors to increase calcium deposition in the bone matrix and decrease the activity of bone resorption.
Physical treatment

In addition to pharmaceutical intervention, lifestyle modifications can promote bone health. Individuals with a moderate risk of osteoporosis are primarily treated with lifestyle modifications. It entails educating at-risk patients to maintain good posture, guarantee adequate mobility and limb flexibility, and preserve the functional capacity of the bones.
Educating patients about potential risk factors and motivating them to limit modifiable risk factors is also a crucial component of the treatment.
