Reasons for Eye Migraine
There is no definitive answer as to what causes Ocular Migraine, but scientists continue to investigate. Doctors believe it is caused by spasms and a lack of blood and oxygen supply to the retina or the rear of the eye, despite the existence of numerous theories to the contrary. However, some physicians believe that a problem in the visual cortex may be the cause of migraine. (4)
Among the potential causes of spasm and in some cases ocular migraine are the following:
Disorders
Certain diseases can also contribute to the development of an ocular migraine. To treat this form of ocular migraine, one must first discover a cure for the underlying disease.
The Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune disease in which the white blood cells begin to attack the tissues of the body. 70% of individuals with lupus suffer from neurological disorders, including ocular migraine. There is no definitive explanation for why people with lupus experience migraine-like headaches and ocular migraine, but it is possible that since the white cells begin attacking the host body, the muscles and arteries surrounding the eyes and retina undergo numerous changes, causing ocular migraine. In addition to contributing to photophobia, lupus makes the eyes and vision cortex more sensitive to light, making the patient more susceptible to ocular migraine.
Plaque buildup in the arteries
Occasionally, due to coagulation, insufficient blood supply reaches the brain, resulting in ocular migraine. Extreme complications may result in a stroke or total loss of vision. This obstruction may be the result of an inherited artery thickening disease called CADASIL (Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy). During CADASIL, the blood flow from the heart to the brain is disrupted, resulting in a diminished blood supply to the brain and areas surrounding the eye, which causes Ocular Migraine.
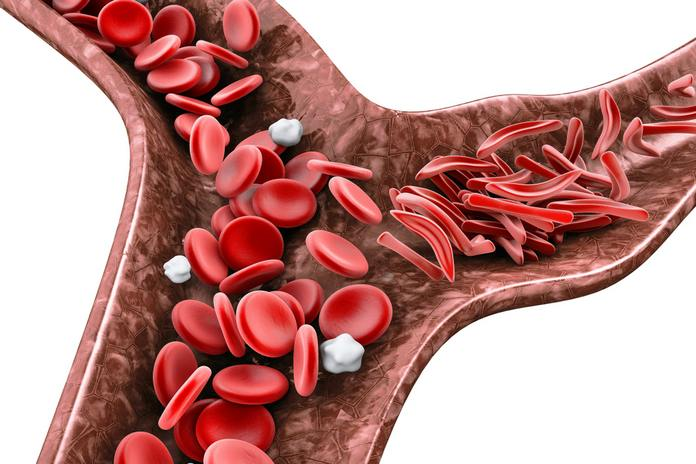
Sickle cell anaemia
A genetic mutation in the HBB gene causes sickle cell disease, which alters the morphology of the red blood cells. This shape prevents the red blood cells from transporting enough oxygen. In addition, this shape damages the red blood cell membrane, resulting in their premature annihilation. This sickle-shaped cell can easily obstruct the arteries and capillaries and form clots around the eyes and brain, causing the arteries to rupture due to increased pressure and causing damage to the visual cortex. Early cell death also causes anaemia, which contributes to the development of ocular migraine.
Idiopathic epilepsy
People with epilepsy are twice as likely to experience ocular migraines as those without the condition. In epilepsy, the brain endures a sudden chemical transformation that causes an increase in brain electrical signals. This abnormal brain activity affects distinct regions of the visual cortex. There are also claims that migraine could be the cause of epilepsy in some individuals, but there is no evidence to support these claims.
Arteritis of the temporal arteries
Temporal arteritis, also known as giant cell, is a disorder characterised by inflammation-induced arterial injury. Temporal arteritis is the name given to inflammation that primarily affects the temples of the skull. The inflammation damages the eye and optic nerve, thereby increasing the pressure on the brain required for clear vision. This inflammation also decreases the blood and oxygen supply to the eye, which is the primary cause of vision issues, auras, and ocular migraine.
Antiphospholipid illness
Antiphospholipid is an autoimmune disease in which healthy body tissues are attacked by antibodies produced by the body. This elevated level of antibodies can obstruct capillaries, preventing blood from reaching the brain and resulting in neurological disorders. These neurological conditions can result in ocular migraine.
Molecular genetics
Although normal migraine and ocular migraine are distinct terms, physicians believe that they may be caused by the same genetic mutation. People with a strong family history of genetic mutations are more likely to suffer from migraine with aura and severe symptoms, and to be diagnosed with migraine at a younger age. According to research published in The Journal of Headache and Pain, TRESK, FASPS, and CADASIL gene mutations are among the leading causes of ocular migraine and migraine with aura.
Family ancestry
Those who have a family history of ocular migraine are more likely to develop the condition themselves. A survey indicates that Ocular migraine and migraine with aura are inherited conditions. Those with a family history of brain hyperexcitability are more likely to develop ocular migraine. The hyperactive brain is more sensitive to sensory input, which disrupts the chemical and nervous signals that cause an ocular migraine. According to a World Health Organisation study, 70% of all ocular migraines are inherited.
The gender
Migraine of the eye is more prevalent in women than in males. This is because women experience greater hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause than males do. In addition, the menstrual cycle and hormonal alterations occur earlier in females than in males.
Human hormones
Hormones facilitate the exchange and transit of information between the brain and the body. According to a study, ocular migraine is caused by hormonal changes in the body that make cells more sensitive. Before the menstrual cycle, the oestrogen and progesterone levels drop, causing ocular migraine in females. Ocular migraines are caused by changes in the masculine sex hormone, testosterone. Any fluctuation in hormone levels can cause migraines.
Age
People between the ages of 30 and 40 are susceptible to developing ocular migraine. Age-related aggravation of the symptoms of ocular migraine is also observed. Age-related decline in the production of hormones such as oestrogen and testosterone, which are responsible for regulating chemical alterations in the brain, is one possible explanation. Any uncontrolled chemical change can induce ocular migraine by contracting the arteries and nerves.
