LASIK pathophysiology
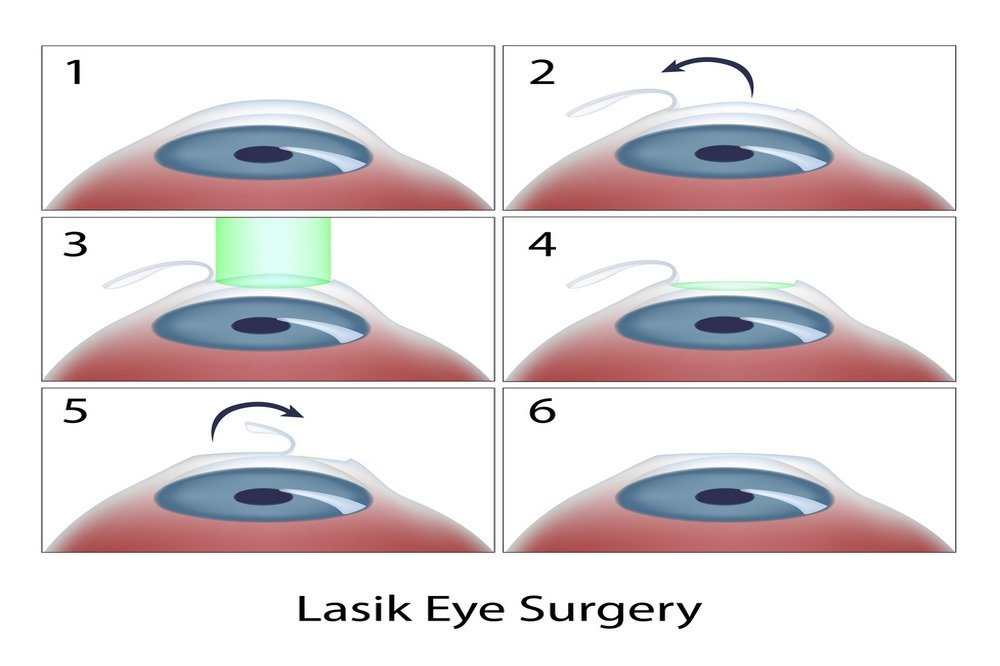
During LASIK, a surgeon with a special qualification in eye surgery will first draw a thin and precise flap of corneal tissue in a hinged fashion using a microkeratome. The surgeon will then pull the hinged corneal flap back to reveal the underlying tissues. Using the excimer, the surgeon then reshapes each cornea with a unique, precise pattern. The surgeon gently repositions the flap on the corneal surface without using any sutures. The actual time of the procedure may vary, depending on how much correction you require.
Lasik surgery uses an excimer laser, a state-of-the art laser that can improve vision and correct refractive error, and eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses. The laser procedure for LASIK alters the shape of your cornea. This is a transparent covering on the front of your eye. Loannis Palalikaris, a Greek scientist from 1991, was the first to create LASIK. The excimer laser had been in use for a few years. Refractive error is the mismatch between the optical system and the lens. This leads to blurred images at some point.
The focusing system in the eye is formed by the front surface of the cornea and the lens inside the eye. Lenses and corneas are responsible for focusing incoming light rays onto the retina’s surface, similar to how camera lenses focus lights on film. Lens and cornea power in the human eyes are perfectly matched to the image and eye length for a focused picture. Any changes to this perfect optical system can lead to refractive error and vision problems. LASIK surgery usually takes ten minutes total in the operating rooms. The surgeons use the laser less than a minute per eye during your time in the operating room.
Lasik is a popular and common procedure to correct refractive errors. Laser-assisted In Situ Keratomileusis, or Lasik, can replace contact lenses and glasses to correct eye sight problems. Special lasers are used to alter the transparent dome tissue of the cornea. In a perfect optical system, the cornea bends or refracts light onto the retina on the back side of the eye. In the case of myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), or astigmatism (farsightedness), light is not bent correctly, resulting in blurry vision and images. (3)
Contact lenses and glasses can correct blurred or altered vision. However, reshaping the cornea can be the key to achieving maximum refraction. You must already be wearing glasses or contact lenses if you’re considering LASIK. You will be guided by a specialized eye doctor or surgeon to determine if LASIK is right for you. Other similar surgical refractive techniques may also correct your vision problems.
