Melanoma
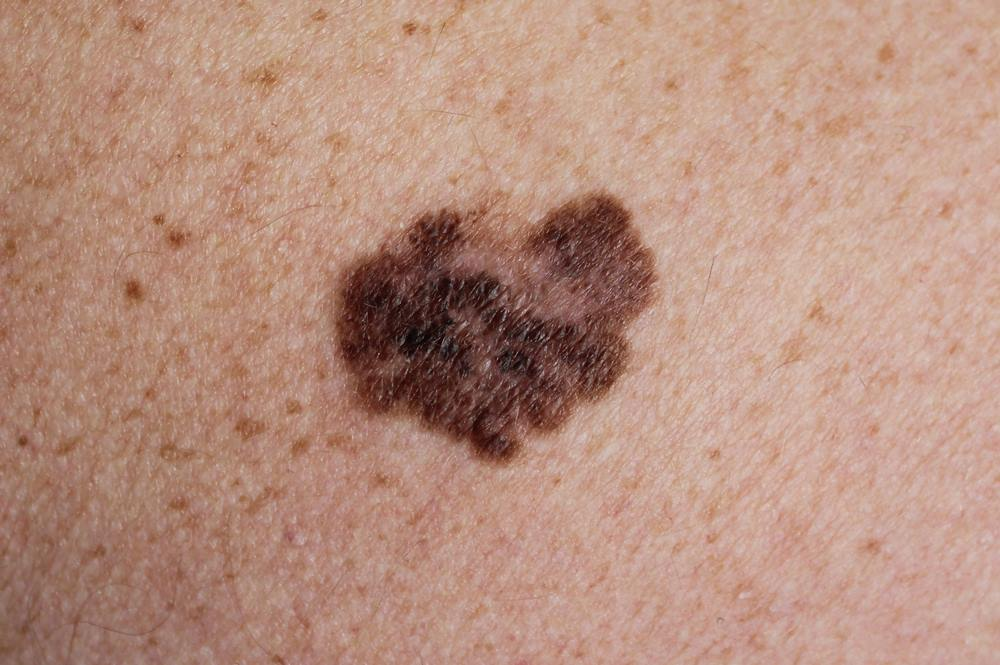
The current treatment for melanoma cancer depends on the prognosis and time of diagnosis. In the case of an early diagnosis of melanoma, the melanoma tumor is surgically removed. If the findings of a lymph node biopsy indicate that malignant cells have spread to lymph nodes, a combination of treatments is the only option. Immunotherapy for melanoma effectively reduces the size of the tumor and increases the survival rate. FDA-approved immunotherapy therapies for melanoma number close to seven. The list of FDA-approved immunotherapy treatments is as follows:
Immunomodulating agents:
The drug Atezolizumab
Atezolizumab is a checkpoint inhibitor that helps target the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway, and it can be used in combination with vemurafenib and cobimetinib to treat melanoma.
The Aldesleukin
Aldesleukin is a cytokine that aids in the treatment of advanced melanoma by targeting the IL-2R/IL-2 pathway on malignant cells.
The drug Ipilimumab
Ipilimumab is a checkpoint inhibitor that targets the CTLA-4 pathway, and the FDA has approved it as a first-line immunotherapy for patients with advanced melanoma.
Interferon 2b
Interferon alfa-2b is a cytokine molecule that inhibits the IFNAR1/2 pathway and is used to treat melanoma patients.
The drug Pembrolizumab
Pembrolzumab is one of the checkpoint inhibitor classes that targets the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway and can be administered to patients with advanced melanoma as well as prior to surgery.
The drug Nivolumab
Nivolumab is a checkpoint inhibitor that combats cancer cells on the PD-L1/PD-1 pathway, and it can be combined with ipilimumab to treat advanced melanoma patients more effectively.
Peginterferon -2b
It is a cytokine that destroys cancer cells via the IFNAR1 pathway and is one of the most effective treatments for melanoma patients.
Oncolytic viral treatment:
T-VEC
T-VEC is a modified form of the herpes simplex virus (HSV) that infects and facilitates the death of tumor cells. T-VEC is most effective for advanced melanoma patients.
