The Importance of Metabolism
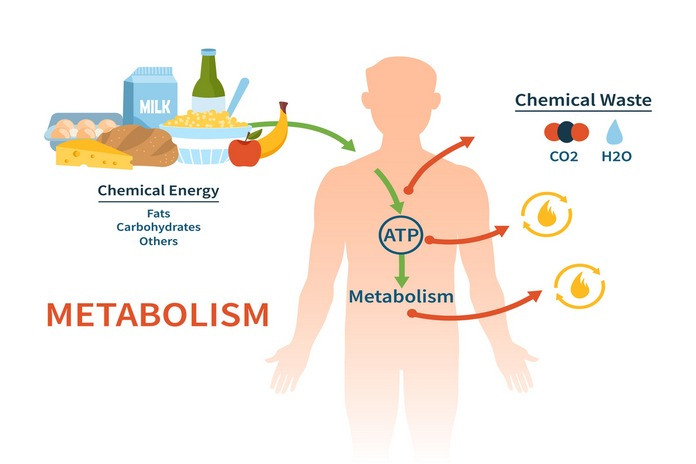
The metabolism is how our body converts what we eat into energy. This process is essential for everyday activities such as breathing, walking and digestion of food. The metabolism also maintains your body’s temperatures and promotes growth and development.
The age, height and weight of a person, as well as their sex, can all affect your metabolism. How your metabolism functions is also affected by genetics and how active you are. Some people have a quicker metabolism than others. This means that their bodies burn more calories every day.
Age
Age is one factor that can affect the speed of metabolism. As people age, their metabolism slows down. Weight gain can result, even when people eat the same amount as they did in their youth. People can take a few steps to keep their metabolism working efficiently as they get older. Sleep is just as important as diet and exercise. People who are well rested have a more efficient metabolism. Dehydration, which can slow the metabolism, is also important.
Gender
It is interesting to see the connection between metabolism and gender. Scientists have known for years that men and woman process food differently. The hormones in men and women are different. Different metabolisms can cause weight gain or lose in both genders.
Men have a faster metabolic rate in general than women. Men burn more calories when they are at rest. Men are therefore more likely than women to lose weight easily and quickly. Men are also more likely than women to store extra calories as fat.
The hormones that are present in women and men can explain these differences. The dominant hormone in men is testosterone. This hormone helps the body break down food and utilize the energy it contains more quickly.
Genetics
The genetics of your body determines the efficiency with which it converts food into energy. Genetics can sometimes determine which foods your body will process better or worse. Some people are genetically predisposed to obesity because they process sugars and carbohydrates more efficiently. Knowing your genetics and metabolism can help you to make better decisions about what you eat, and how much exercise you need to do to maintain a healthy body weight.
Physical Activity
Physical activity has been shown to play an important role in weight loss and metabolic health. Regular physical activity helps with weight loss, maintaining a healthy body weight and improving insulin sensitivity. Physical activity can increase the metabolism. The body’s metabolism is how it burns calories. This means that people who are physically fit tend to have higher resting metabolism rates, which means they burn more calories even when not actively moving. This can improve your health and help you lose weight.
Muscle mass
The equation for weight loss is straightforward: you must burn more calories than what you consume. What if this is not accurate? What if your muscle mass also impacts your metabolism?
Muscle mass plays a part in metabolism. The more muscle mass you have, you will burn more calories at rest. It is because muscle tissue requires energy to maintain. In contrast, fat is an inactive tissue that doesn’t need as much energy.
If you want to lose weight, then building muscle mass can help increase your metabolism. You can’t eat anything and expect to lose weight. You need to create a deficit of calories by burning more than you consume.
Smoking
Smoking is associated with many health issues, such as an increased risk of cancer, stroke, and heart disease. Did you know that smoking could also affect your metabolism.
Smoking slows down metabolism and makes it difficult to maintain or lose weight. Smokers are more likely than non-smokers to be overweight. Smoking increases the risk of metabolic syndrome. This condition is characterized by several risk factors that can lead to heart disease or diabetes. These factors include high cholesterol and blood sugar, as well as high blood pressure.
