What is your Metabolic Type?
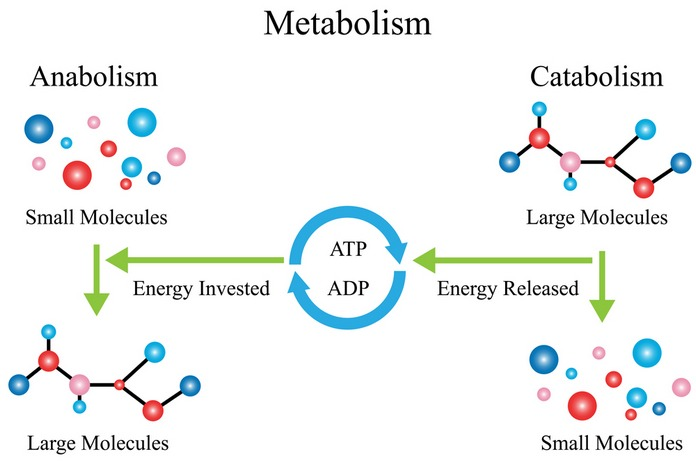
The process by which your body converts the food that you eat to energy is called metabolism. There are three different types of metabolism: anabolism (catabolism), aerobic and anabolic. The catabolic metabolism reduces large molecules to smaller ones and releases energy. Anabolic metabolism requires energy to build complex molecules out of small molecules. Aerobic metabolism converts food into energy using oxygen.
Catabolism
Catabolism is the breakdown of organic molecules into smaller parts. This process releases energy that the cell can utilize to perform its functions. Catabolic pathways begin with the addition of a water-molecule to the molecule that is being broken down. Hydrolysis is the process that makes it easier to break down the molecule. All cells contain enzymes that catalyze the majority of these reactions.
Catabolism produces small molecules which can either be used in the cells or excreted by the body. Catabolism releases energy in different ways depending on how chemical bonds are broken. Some reactions produce heat, while others release electrons which can be used to create ATP.
Catabolism: Its role
What comes to your mind when you think about energy? Food is what comes to mind for most people when they think of energy. We need food to survive, and it gives us the energy needed to breathe and move. Where does this energy originate?
In our bodies, food is broken down into glucose molecules. Glucose fuels our lives. Catabolism is the breakdown of food into glucose.
The catabolism process is divided into two stages: digestion and absorption. Digestion is the process of breaking food down into smaller pieces to allow it to be absorbed in the bloodstream. Absorption occurs when these tiny pieces are transported through the intestinal wall into the bloodstream.
Anabolism
The body builds larger molecules by anabolism. These larger molecules, which include proteins and lipids as well as nucleic acid and RNA, are necessary for the body’s proper functioning. This process can be used to create new molecules, such as DNA and proteins. The cell must have energy to perform anabolism. Glucose is the most common energy source for cells.
Anabolism is also known as constructive metabolism. Constructive metabolism occurs when the body breaks down the food in order to produce energy and create new tissue. To perform these functions, the body needs to consume a wide variety of nutrients. For a healthy metabolism, carbohydrates, proteins and fats are essential.
The body needs carbohydrates to produce glucose which is then used for energy. Glucose plays a vital role in the nervous system and brain. Carbohydrates are more efficient than protein or fat as an energy source. The body needs proteins to create new tissues, such as muscle, hair, skin and nails. Also, they play a part in the repair of damaged tissues. Fats are essential for cell membranes, among other functions.
The role of anabolism
The process of anabolism is to build molecules by combining smaller units. The process is responsible for tissue growth and repair. During the anabolism process, small molecules combine to form larger molecules. These larger molecules are necessary for the body’s proper functioning.
Proteins are among the most important anabolic molecule. Amino acids are the smaller units that make up proteins. Twenty different amino acids can be used to make proteins. Some aminoacids can be produced by the human body while others are obtained through food.
The body relies on proteins for many of its functions. They play a role in the structure and functioning of tissues, organs, and cells. They are also involved in metabolism, energy generation, and immunity.
Aerobic metabolism
Aerobic metabolism uses oxygen as a source of energy for the cells. Cells in the body use this type of metabolism to create adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), which is the main energy source for cells. Aerobic metabolism is slow and steady, which can provide energy for a long time.
It is through the aerobic system that we can exercise for long periods of time. The aerobic system breaks down glucose, amino acids and fatty acids through a series chemical reactions. These molecules can then be used as energy by cells. These reactions occur inside mitochondria which are found within the cytoplasm of cells.
The role of aerobic metabolism
This type of metabolism occurs when the body must generate large amounts of energy rapidly, as it does during exercise. The aerobic system creates energy by using glucose and fatty acid from food. As a by-product, carbon dioxide and water are produced.
