Stiffening Of Muscles
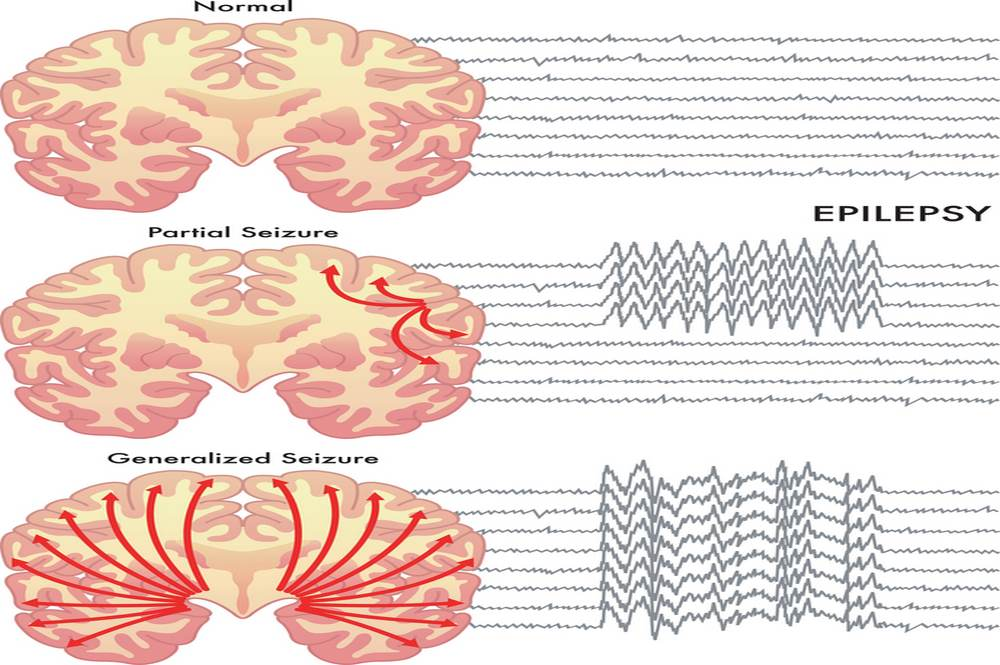
In a tonic-clonic seizure, episodes of increased muscular jerks, the clonic phase, are punctuated by periods of increased muscle rigidity, the tonic phase. Muscles become rigid when an initiating neural stimulus is interrupted or when an inhibitory stimulus is prolonged. The patient may characterise the sensation as increased muscle rigidity that inhibits free and fluid movement. During slumber, a sudden stiffening of the body may occur. A person who experiences a seizure with muscle rigidity while standing may collapse. This rigidity is also short-lived and tends to subside as the seizure’s effect fades off.
