Stroke
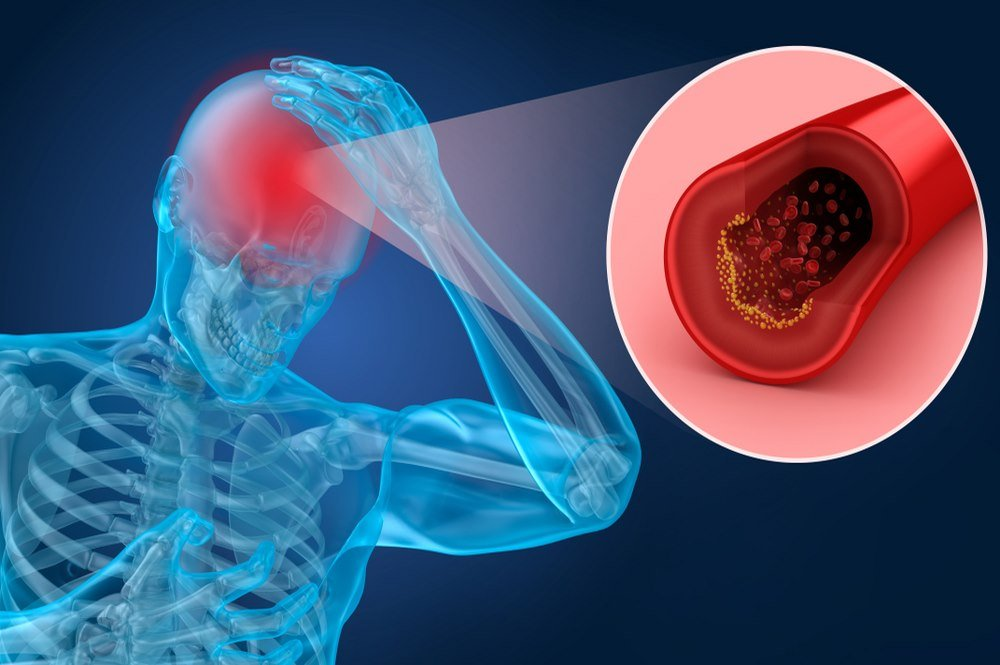
Stroke is the most prevalent known cause of epilepsy in the elderly population. Due to a blood clot, decreased blood flow to the cerebral tissue causes a stroke. An immediate seizure following a stroke is not inherently indicative of epilepsy. Stroke is identified by the occurrence of multiple convulsions in the patient’s past medical history. Epilepsy is commonly associated with hemorrhagic stroke, which involves haemorrhage. Brain damage caused by a stroke in the cerebral region, which comprises the majority of the brain and regulates essential motor functions, is more strongly associated with a later diagnosis of epilepsy.
