Airway Management
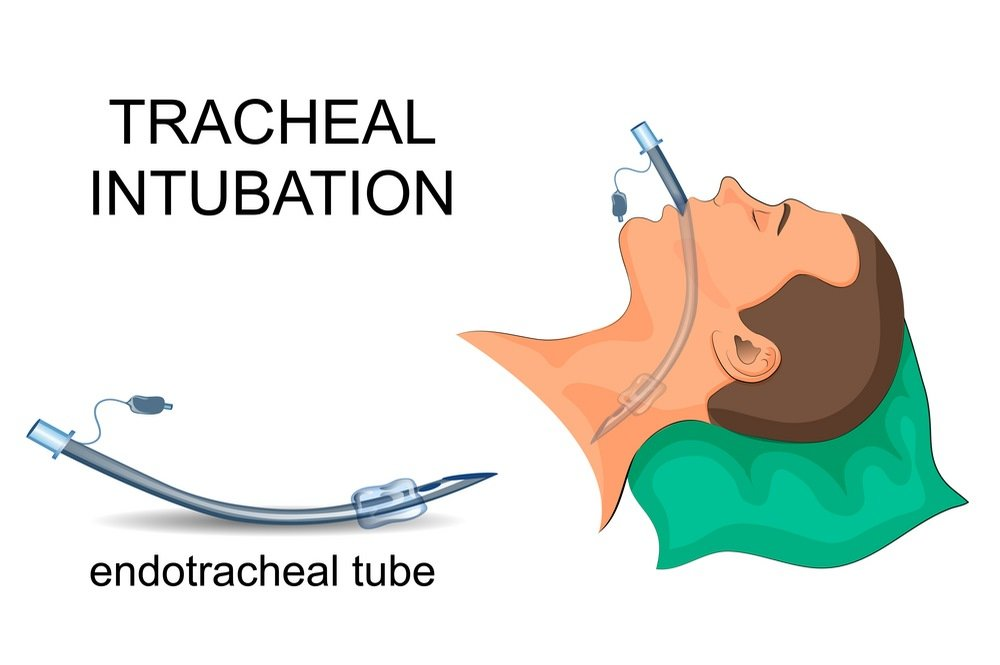
Anaphylaxis can produce swelling of the tongue, lips, throat muscles, and voice box. In addition to edoema, anaphylaxis can hyperstimulate airway secretion. This can significantly impede respiration. In order to treat this respiratory obstruction, the airway can be reopened using a technique called intubation. Intubation entails inserting a catheter into the airway.
Then, oxygen can be administered to further facilitate respiration. Indicative of oxygen therapy is cyanosis, which manifests as bluish lips and pallid skin due to loss of blood volume. A ventilator is used to facilitate the patient’s breathing. Proper respiratory preservation prevents respiratory arrest and possible mortality resulting from it.
