Gout is one of the most common forms of arthritis that causes severe joint pain, stiffness, and edoema. Typically, the joint in the big toe is affected by gout. It is a complicated and extremely common form of arthritis that can affect anyone. Gout is characterised by severe and sudden attacks of joint tenderness in multiple joints. A gout attack may occur unexpectedly, causing you to awaken in the middle of the night with a searing sensation in your big toe. Gout causes the afflicted joint to become so hot, tender, and swollen that the weight of your blanket may become unbearable. Later episodes of joint pain are likely to affect additional joints encircling the affected joint and to last longer.Symptoms of gout may fluctuate, but there are methods to manage the symptoms of the disease and prevent flare-ups. Symptoms and signals of gout occur suddenly and predominantly at night. Gout can affect any joint, but in the majority of patients, it affects the big toe. Other frequently affected joints include the wrists, elbows, ankles, fingertips, and knees. Within the first hour to 12 hours following the onset of gout disease, the pain is most likely to be severe. After the most severe pain subsides, there may be some joint discomfort for several days to weeks. Most patients suffer from gout due to an excess of uric acid in their bloodstream.
As gout progresses, a person may lose the ability to move his joint normally. If you are experiencing severe and sudden joint discomfort, you should consult a physician about gout. Without appropriate treatment, gout can cause severe joint damage and intensify joint pain. After a gout attack, the patient’s range of motion is restricted, making it difficult for them to conduct normal daily activities. If you are experiencing inflammation or discoloration in your joints, as well as fever, which can be a sign of infection in the body, you should seek immediate medical attention. Typically, specific medications are used to treat gout and manage its symptoms.
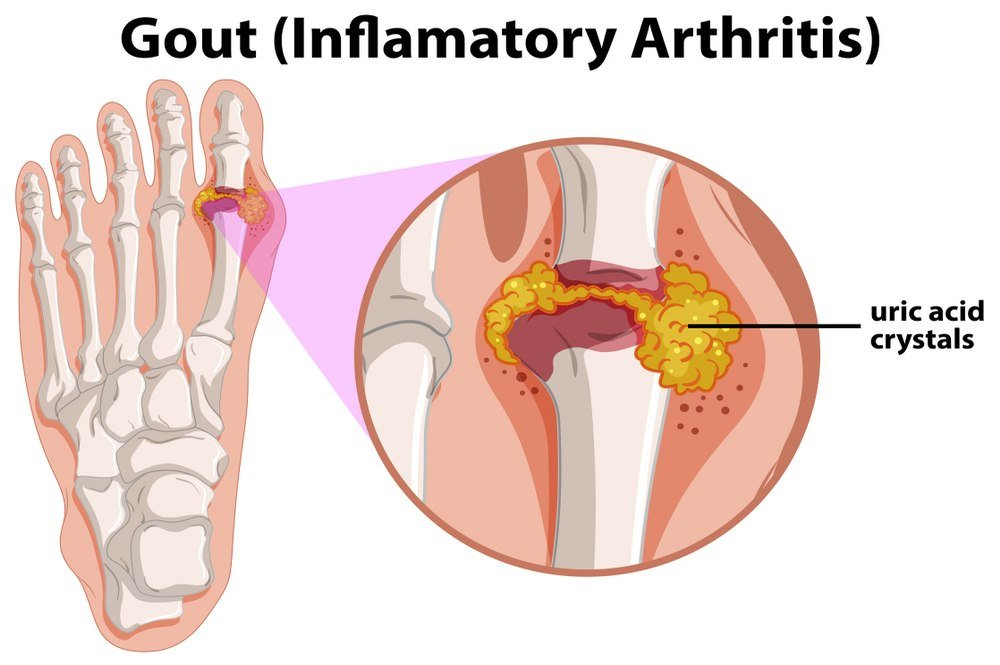
Attacks of gout can come and go rapidly, and in some cases recur over time, indicating that there is gradual tissue damage in the area of inflammation. The precise cause of gout is unknown, but obesity, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease are risk factors. Men are more likely to develop gout than women after menopause, but men are at a greater risk of developing gout. The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that approximately 8.3 million Americans suffer from gout annually. The symptoms of gout are caused by the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints and the body’s reaction to the formation of these crystals.
