Frequent Causes of Sharp Wrist Pain
There are numerous possible causes of wrist discomfort. Carpal tunnel syndrome, overuse injuries, and fractures are the most prevalent. (3)
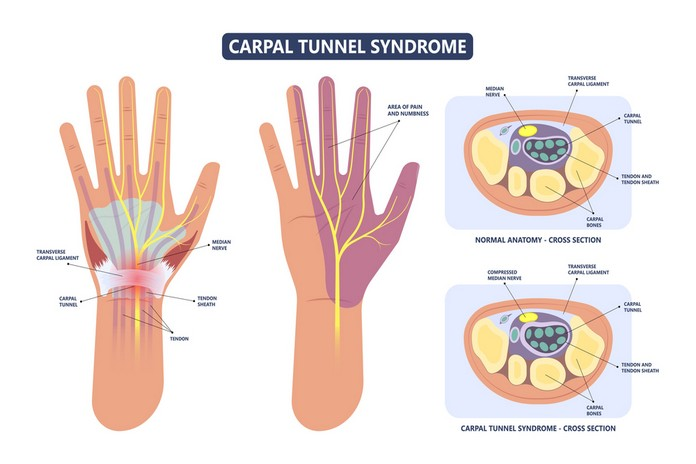
Carpal tunnel disorder
The median nerve is compressed as it passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, resulting in carpal tunnel syndrome. CTS is characterized by numbness and tingling (pinprick sensations) in the hand and digits, pain in the hand or arm, hand weakness, and difficulty gripping objects. These symptoms can differ from person to person and can manifest intermittently.
The symptoms are brought on by pressure on the median nerve as it traverses the carpal tunnel, a narrow passageway in the wrist. It is estimated that 3-6% of the U.S. population suffers from carpal tunnel syndrome, making it one of the most prevalent nerve disorders causing wrist discomfort. It is more prevalent in women than in men, and is most prevalent between the ages of 30 and 60.
Overuse accidents
Overuse injuries can occur when the forearms are used excessively or incorrectly. They can cause forearm pain, swelling, and stiffness.
If you are experiencing wrist pain, it is likely due to an overuse injury. The repetitive motions of activities such as typing, using a mouse, and gripping a tool can lead to wrist inflammation and discomfort.
It is crucial to visit a doctor to determine the cause of wrist pain caused by overuse and to receive the appropriate treatment. There are essential measures you can take in the interim to alleviate the discomfort and inflammation caused by the condition. Ice the affected area for 15 to 20 minutes multiple times per day, take over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed, and don a brace or splint if instructed to do so by your physician.
Fractures
Fractures are a frequent cause of wrist discomfort. A fracture of the wrist is a split in one or more of the wrist’s bones. A fracture can occur when a person falls and lands on an outstretched hand, or when the hand is struck against an unyielding surface. The fracture of the radius, which is the larger bone on the thumb side of the forearm, is the most common wrist fracture. A broken ulna, the smaller bone on the side of the forearm opposite the little finger, is another prevalent type of wrist fracture.
Wrist fractures are extremely prevalent and can be caused by a variety of traumas. Pain, edema, and bruising are the most typical symptoms of a wrist fracture. You may also observe that your wrist is less flexible than it once was. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention immediately. In most cases, a wrist fracture can be treated with rest and cold, but in some instances, surgery may be required.
Wrist fall
Wrist drop is a potential complication of wrist pain in which the digits become limp and unable to be straightened. This can make routine activities such as opening a door or picking up a cup problematic.
Damage to the nerves that travel through the wrist or arm may cause wrist drop. This injury or condition, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, polio, or diabetes, can cause this damage. Some drugs can also cause wrist decline by causing nerve damage.
Consult your doctor if you are experiencing wrist discomfort to determine the cause and the most effective treatment. If you have been diagnosed with wrist drop, you may have access to treatments that can enhance your mobility and quality of life.
Rheumatoid arthritis
If you have wrist pain, you may ponder if it’s due to arthritis. Arthritis is a prevalent condition that causes joint inflammation and discomfort. It can affect any of the body’s tiny joints, including the wrist.
Several types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout, can produce wrist pain. Each form of arthritis has its own symptoms and underlying causes.
Wrist pain is the most prevalent symptom of arthritis. The discomfort may be dull or achy and intermittent. Other symptoms include wrist joint swelling, redness, warmth, and rigidity.
Gout
Uric acid is a compound produced by the organism when purines are broken down. Many foods contain purines, including red meats, seafood, and alcohol. When uric acid levels become excessive, crystals can form and form kidney stones. Additionally, uric acid can accumulate in other tissues and fluids of the body, such as the joint spaces, causing gout. This can result in inflammation and discomfort.
One of the joints most commonly impacted by uric acid crystals is the wrist. Gout can cause severe discomfort that may prevent you from using your wrist normally. Medication to reduce uric acid levels and ice or heat therapy to reduce inflammation and discomfort are used to treat gout.
Ganglion polyps
A ganglion cyst is one potential source of wrist discomfort. Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on the body’s joints or tendons. Ganglion cysts occur most frequently on the wrists, ankles, and fingertips.
Ganglion cysts can cause pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the afflicted area (wrist joint in this case). In some instances, the ganglion cyst may impede movement of the joint or tendon it is located on. If you have wrist pain and suspect you may have a ganglion cyst, you should see a specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
inflammatory tendonitis
One of the most common causes of wrist discomfort is tendonitis. Inflammation of the tendons that connect muscles to bones is the cause of this condition. This can result in wrist pain, joint rigidity, and swelling. Tendonitis is frequently caused by overuse or repetitive motions, such as typing or tense gripping. It may also be the consequence of a fall or car accident. Typically, tendonitis is treated with rest, cold, and anti-inflammatory medication. In certain instances, surgical intervention is required to repair damaged tendons.
Kienbock’s illness
Kienbock disease is a disorder affecting the forearm. Unknown, but it is believed that the disease is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the wrist. This can cause injury to the wrist’s bones and ligaments.
Wrist pain is one of the most prevalent symptoms of Kienbock disease. The discomfort may be felt along the side of the wrist and may intensify when the hand or fingers are moved. You may also experience forearm swelling and stiffness. If you have been diagnosed with Kienbock disease, your physician will likely prescribe rest, cold, and medication. In some instances, surgery may be required.
Ligament rupture
Ligaments are stiff connective tissues composed of fibrous material that connect bones to one another. They provide the joint with stability and resilience. A wrist ligament rupture can cause pain and instability.
The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) and the radial collateral ligament (RCL) are the most frequently injured ligaments in the wrist. The ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) connects the ulna bone to the humerus bone and is located on the inside of the wrist. The RCL connects the radius bone to the humerus bone and is situated on the outside of the wrist.
A ligament rupture can be caused by a sudden injury, such as a fall, or by excessive wrist use. Symptoms of a torn ligament in the wrist include pain, edema, and instability.
