Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis
Diabetes is a measurement of blood sugar concentration. This is examined in two distinct methods by physicians:
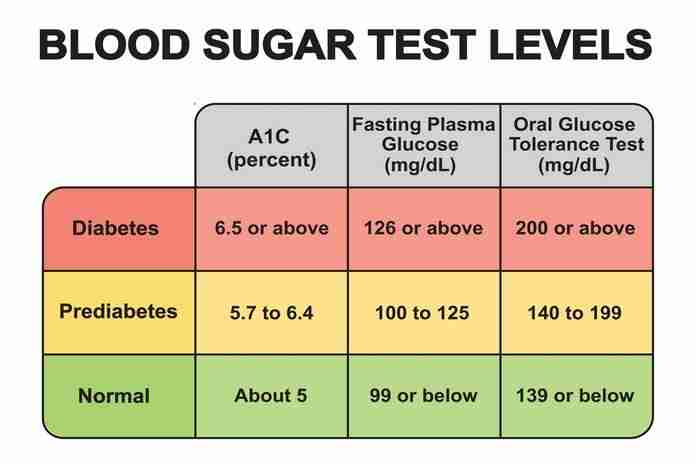
A blood A1C measurement
hbA1C or A1C is a non-fasting blood test that measures the normal quantity of sugar in your blood over the course of the previous three months as a percentage. Consequently, a normal percentage is less than 5.7%, and 6.4% indicate prediabetes. Anything increasing by more than 6.5% indicates that a person has diabetes.
Normal blood glucose testing
This necessitates that you fast before a blood test, so that your endocrinologist or primary care physician can measure the blood sugar level at any given time. Normal fasting glucose levels are 99 mg/dL or less. Therefore, prediabetes must be diagnosed if fasting blood sugar levels are between 100 and 125 mg/dL. While a blood glucose level greater than 126 mg/dL indicates diabetes, a reading greater than 126 mg/dL also indicates diabetes.
Typical range
Therefore, the test indicates the three-month average blood glucose level. This test analyzes the percentage of blood glucose bound to the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells known as hemoglobin. The higher your blood sugar level, the more glucose will attach to your hemoglobin.
In general,
A1C levels below 5.7% are regarded as normal.
A1C levels between 5.7% and 6.4% are indicative of prediabetes.
A1C levels of 6.5% or higher on two separate occasions indicate type 2 diabetes.
Consequently, certain conditions, such as pregnancy or having a common form of hemoglobin, may cause the A1C test to produce inaccurate results, such as when a subject has a common form of hemoglobin or is pregnant.
Test of fasting blood glucose
However, the blood sample is collected only after a fast of nearly eight hours or overnight.
A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher indicates type 2 diabetes.
