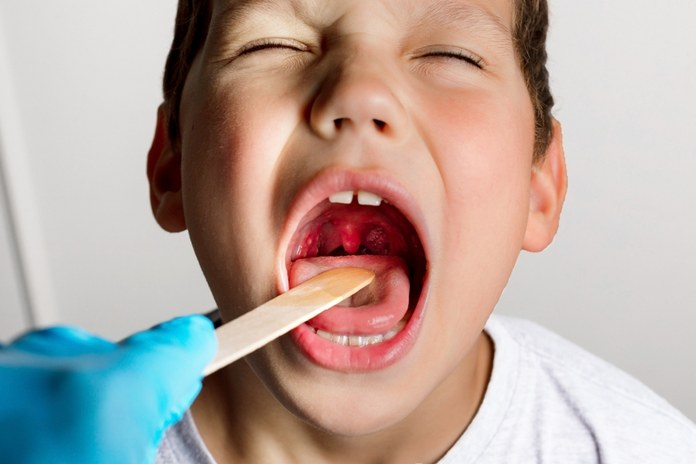
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis, also known as tonsillitis, is an infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. It affects the soft tissues in your throat, including the tonsils. Tonsils are two lumps of round tissue located on either side of your back of mouth. They protect your body by trapping bacteria that enters through the mouth and breathing passages. (1)
The throat feels sore and painful when you have tonsillitis, just like a bad cold. Tonsillitis can also be characterized by peritonsillar infection, quinsy or chronic tonsillitis. It can last a few weeks or days, but antibiotics are effective in treating it. They can be recurring for some people. Untreated, a severe infection can cause serious complications like acute sinusitis and ear infections.
Tonsillitis Types
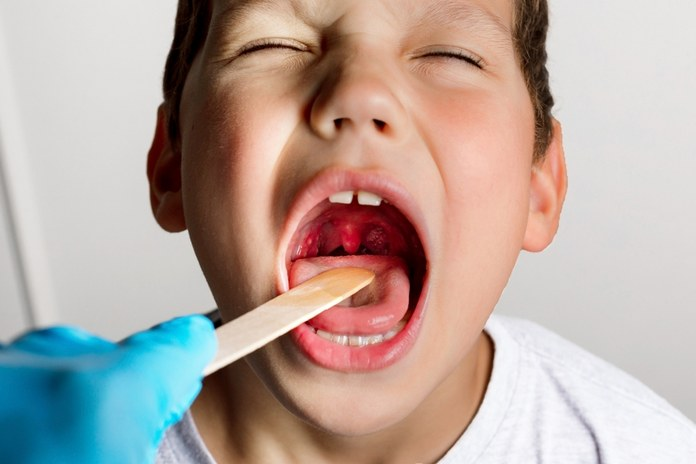
Adults can also get tonsillitis. Tonsillitis can be classified as acute, chronic or recurrent (although there is also an acute on chronic). (2)
Both tonsils and the adenoids produce antibodies that protect the throat from disease germs entering through the mouth or nose. These lymph nodes, therefore, are more susceptible to infection and inflammation caused by viruses and bacteria.
- Acute tonsillitis –Either bacteria or a virus causes it. This is the most severe type of tonsillitis, causing sore throats and high fevers in children.
- Recurring tonsillitis –If you have up to seven episodes in a single year, or three in three consecutive years of the same year, this is called recurrent tonsillitis. In such cases, stopping the antibiotic can cause another infection to occur within a couple of weeks.
- Chronic tonsillitis –As the name implies, chronic tonsillitis is caused by a persistent sore throat or tender cervical nodes.
- Peritonsillar Abscess or Quinsy () When tonsillitis is left untreated, an abscess can develop lateral to tonsil. The peritonsillar area becomes inflamed and swollen. Pathogens that are most commonly found include staphylococci (including Fusobacterium Necrophorum), haemophilus flues, streptococci, and Haemophilus influenzae. No viruses are involved. The symptoms include severe throat discomfort, fever, altered vocal quality, drooling, difficulty opening your mouth, and bad breath.
- Hypertrophy of the Tonsils – Enlargement of the tonsils accompanied by difficulty in speaking, snoring and swallowing.
