Pulmonary embolism is caused by a blockage of one of the pulmonary vessels in the lungs. The majority of pulmonary embolisms are caused by blood clots moving from the deep veins of the legs to the lungs. In rare cases, deep vein thrombosis can also occur from other veins. As blood clots in veins can block normal blood flow into the lungs, it is a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk of death or other serious conditions can be greatly reduced by immediate treatment. Avoiding blood clots on your legs is the best way to prevent pulmonary embolism. [ 1 ]The thrombus causing blockage is a blood clot that lodges into the pulmonary artery and causes blockage of the blood to the lungs in case of embolism. A blood clot usually causes pulmonary embolism, especially in the lower extremities. Blood clots are rarely found in the veins of the upper extremities, the right heart chambers or the pelvic and renal veins. Large blood clots that have reached the lungs can cause hemodynamic compromise by floating at the bifurcation between the lobar branches and the major pulmonary arterial. Although the cause of pulmonary embolism is unknown, certain risk factors can contribute to its development. Blockage of blood circulation due to thrombus may cause serious problems such as blockage in other arteries of the body. This can be fatal, especially if blood oxygen levels begin to drop.
According to several studies, if the pulmonary embolism is not treated properly, it can lead to a high mortality rate in patients who have acute pulmonary emphysema. This death rate could be as high as 30 percent. The mortality rate of patients who receive a timely diagnosis and proper treatment is only 8%. Nearly 10% die suddenly from acute pulmonary embolism. Two of three pulmonary embolism patients die within two hours of the onset of severe symptoms. A pulmonary embolism is caused by a lack in blood flow, which leads to lung tissue scarring and damage. Low oxygen levels in blood can cause harm to other organs.
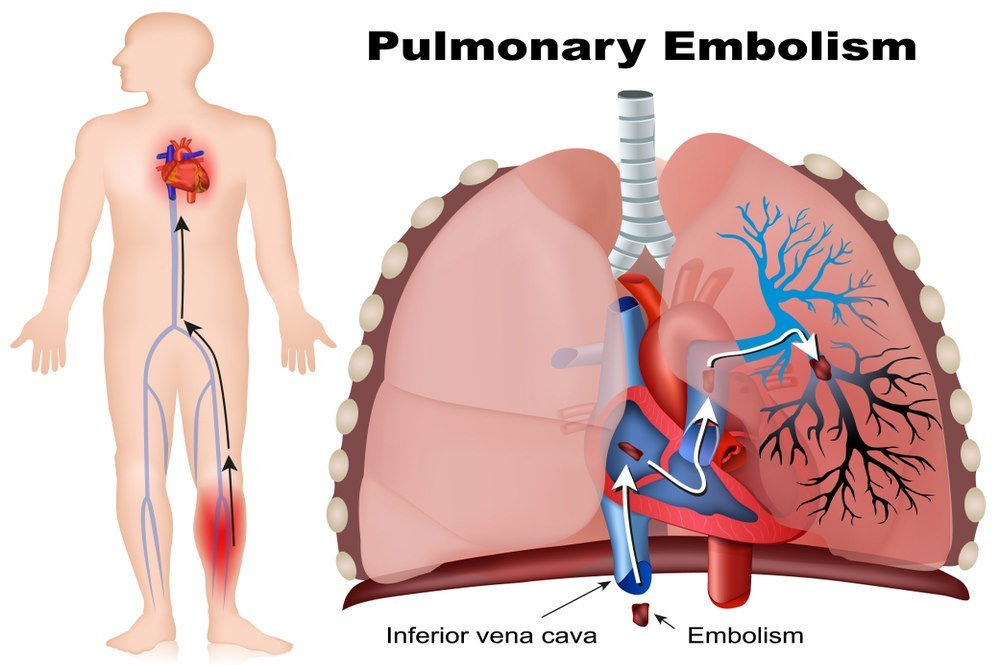
Patients with a severe form of pulmonary embolism can quickly experience life-threatening complications and even die from large blood clots. The majority of patients who suffer from pulmonary embolism will recover completely within a few months or weeks, without any noticeable complications. There is the possibility that long-term complications can lead to mild to severe symptoms. Doctors say that blood clots can also travel through a deep leg vein to the lungs. This is known as deep venous thrombosis. Deep vein thrombosis can occur when legs are resting for a longer period of time, such as during a flight or long drive. It may also happen to patients on bedrest. [2]
